Introduction: The Timeless Elegance of Black and White
Black and white photography is more than just an absence of color; it’s a different perspective on the world. This guide explores how black and white can simplify compositions, direct focus to the subject, and create a strong emotional impact.
Understanding Black and White Composition
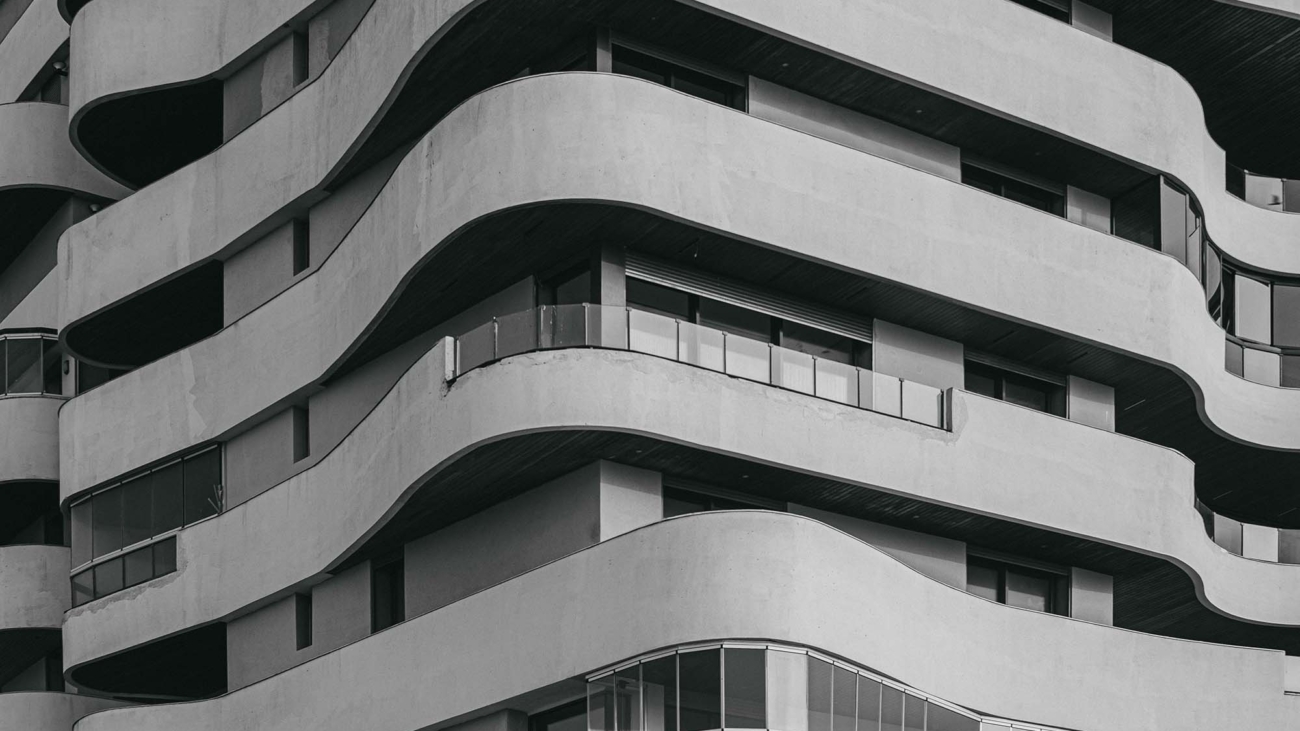
Black and white photography strips away the distraction of color, allowing viewers to focus on other aspects of the photo, such as texture, shape, light, and shadow. It brings out the raw essence of the scene or subject, emphasizing contrasts and subtleties.

Creative Process: Crafting Black and White Images
- Visualizing in Monochrome: Train your eye to see the world in gradients of gray. Look for scenes with strong contrasts or interesting textures that would translate well into black and white.
- Focus on Lighting: Lighting plays a crucial role in black and white photography. High contrast lighting can create dramatic images, while soft, even lighting can convey subtlety and nuance.
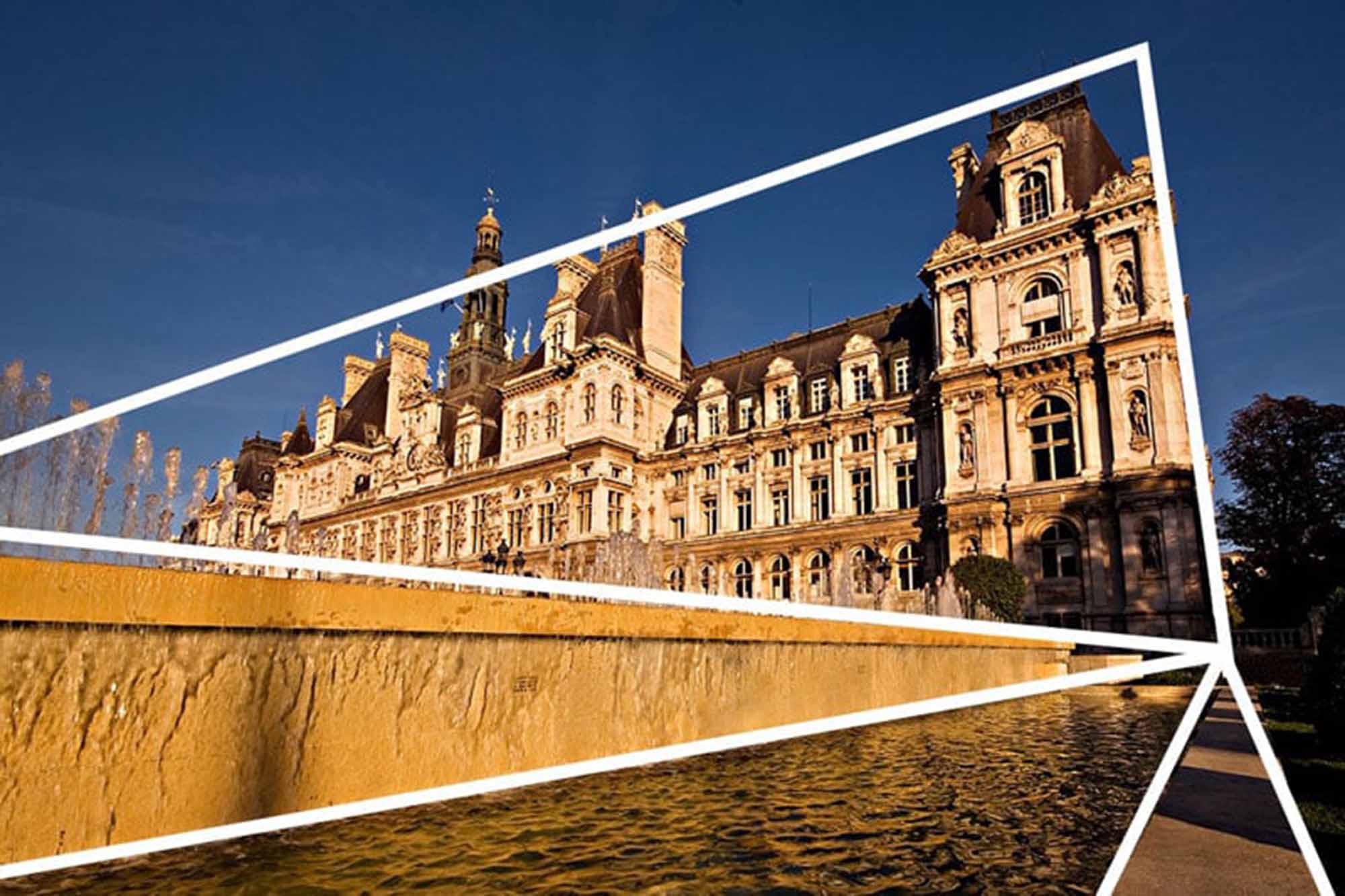
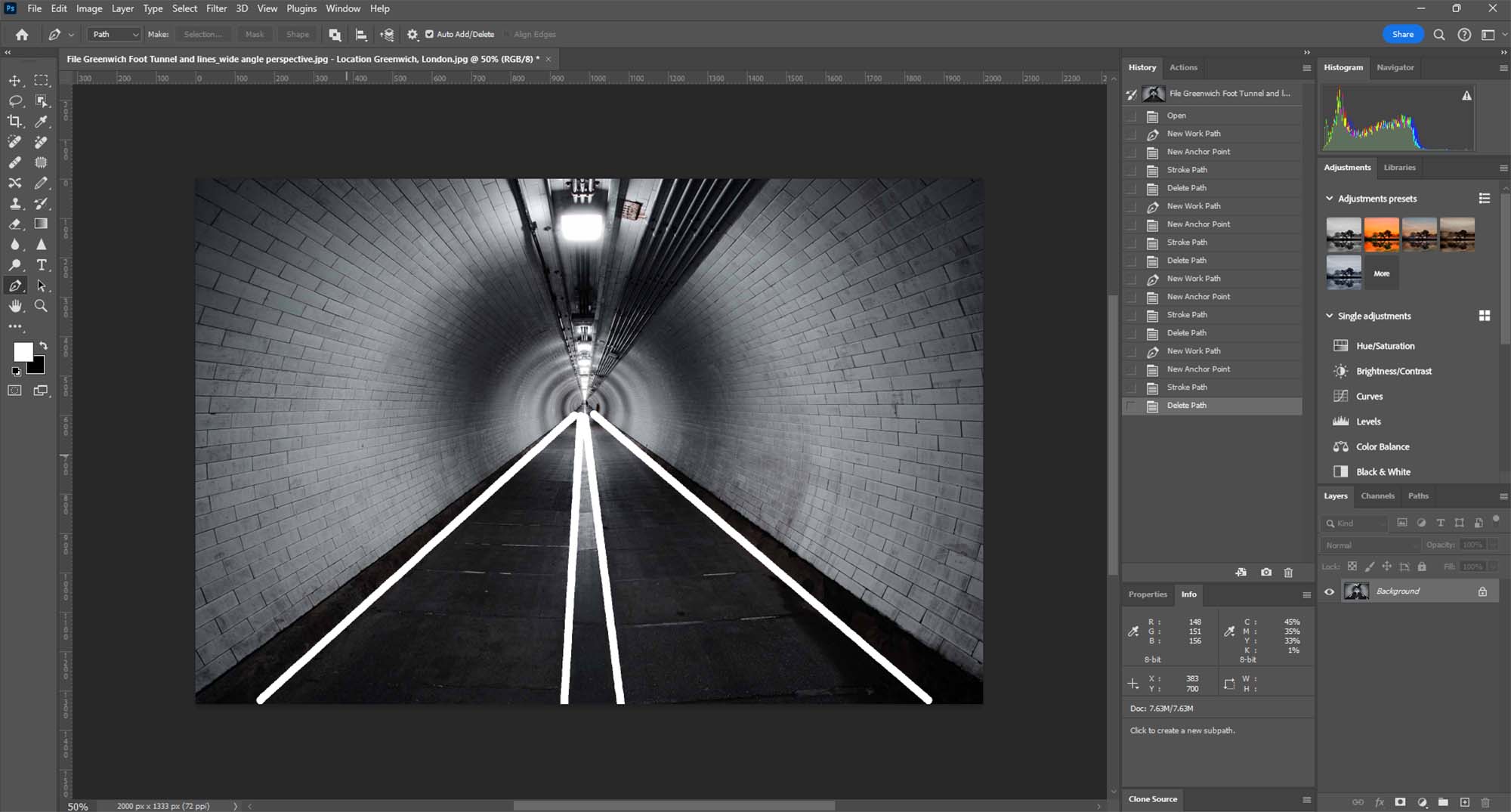
- Composition and Framing: Pay attention to the composition, using elements like lines, shapes, and textures to guide the viewer’s eye.
Tips for Photographers
- Shoot in Color: Capture your images in color and convert them to black and white during post-processing for greater control over tones and contrasts.
- Play with Contrast: Experiment with different levels of contrast to create depth and drama in your images.
- Use Filters: When shooting, use red or yellow filters to enhance contrasts in the sky and landscapes.
- Mind the Grays: Pay attention to the gray tones in your image. They should vary to create a dynamic range in your photo.
Advanced Techniques in Black and White Photography
- High-Key and Low-Key Photography: Explore high-key (predominantly light tones) and low-key (predominantly dark tones) photography for artistic effects.
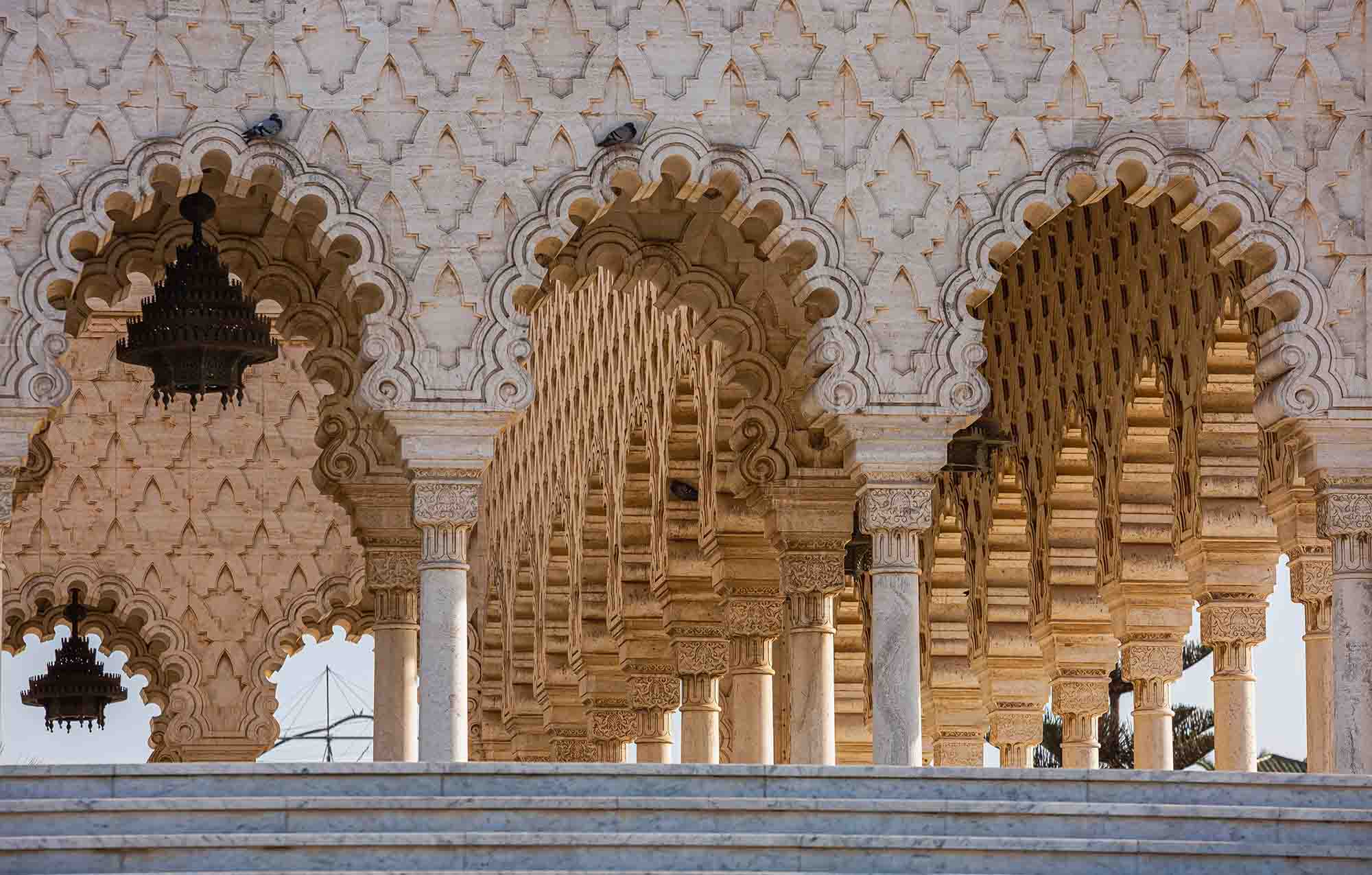
- Texture Emphasis: Use black and white to emphasize textures, bringing out details that might go unnoticed in color.
- Silhouettes and Shadows: Create striking silhouettes and shadow play, which are particularly compelling in black and white.
Practical Applications in Various Genres
- Portrait Photography: Capture the expressions and emotions of subjects, focusing on the play of light and shadow on their features.
- Landscape Photography: Convey the drama of landscapes, from the starkness of barren fields to the intricacy of urban architecture.
- Street Photography: Document the rawness and authenticity of everyday life, highlighting the stark realities of urban environments.
Conclusion: The Power of Monochrome
Black and white photography is a powerful tool for simplifying compositions and conveying stories in a more focused and emotionally charged manner. It challenges photographers to look beyond color and explore the fundamental aspects of light, shadow, and form.