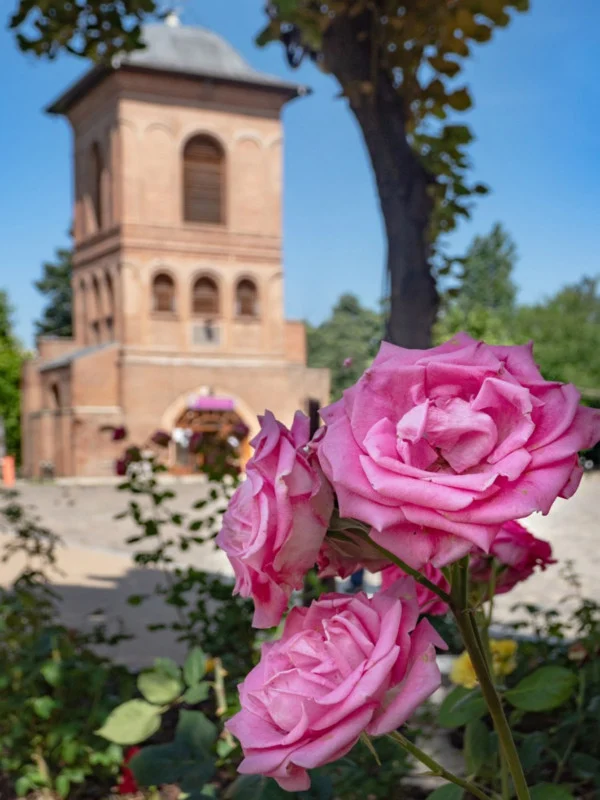
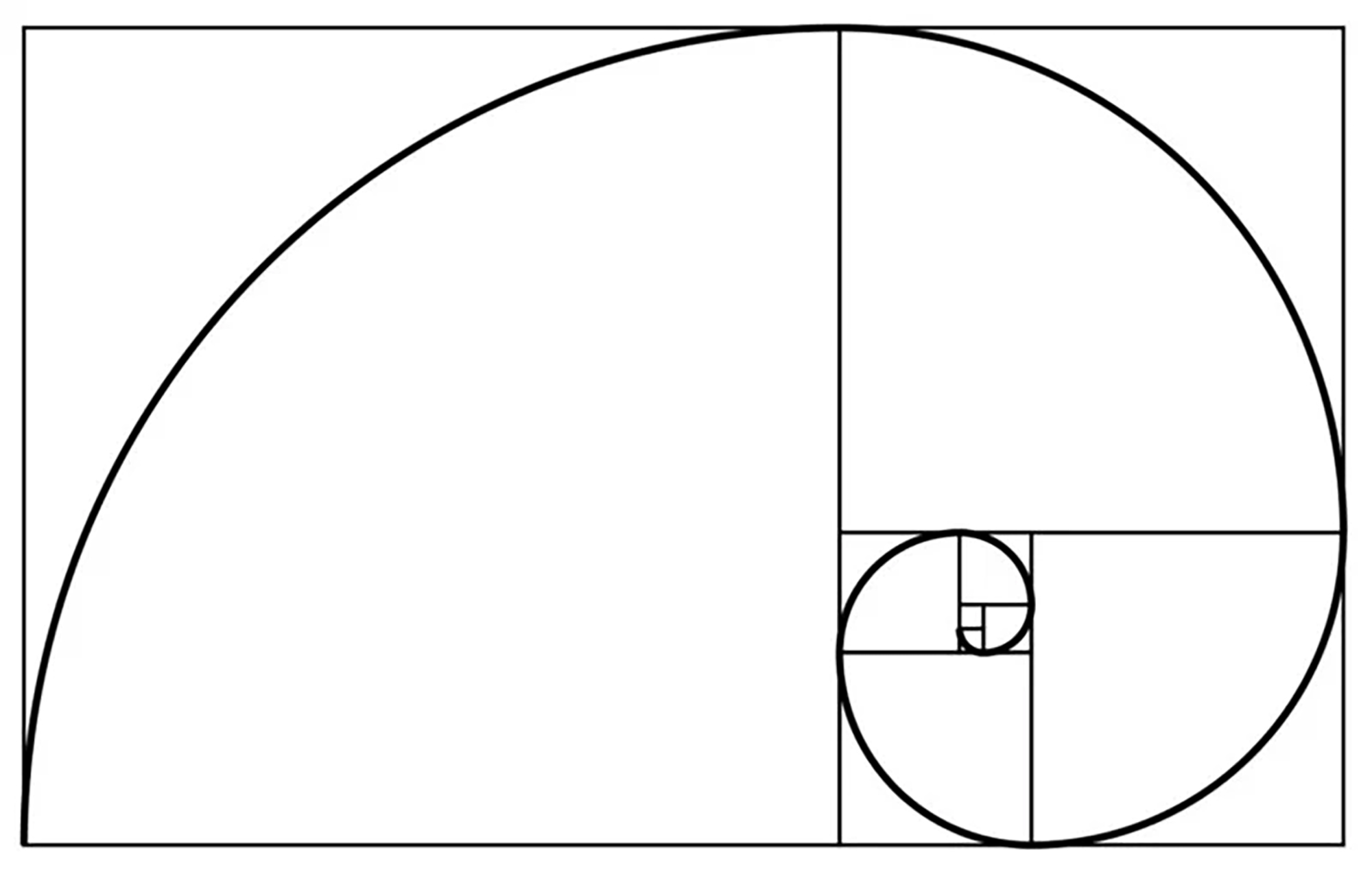
How to Take Captivating Photos Using 32 Powerful Composition Techniques
Whether you’re using a DSLR, mirrorless camera, or just your phone, learning photography composition is the fastest way to take more captivating, intentional photos. Composition is what turns everyday images into visual stories—it’s the art of placing elements with purpose, guiding the viewer’s eye, and creating emotion.
Composition is the silent force that guides your viewer’s eye, stirs emotion, and transforms a moment into a powerful visual story. It’s what separates a quick snapshot from a photograph people remember.
This guide introduces 32 powerful composition techniques—each one designed to improve your photography regardless of gear or skill level. You’ll get a short, practical explanation of each technique, along with a direct link to a full, in-depth article where you can learn more.
Table of Contents
1. Rule of Thirds Photography Composition
Divide your frame into a 3×3 grid and place your subject along the lines or intersections. This simple technique instantly brings balance and focus to any photo.

2. Leading Lines in Photography Composition
Use natural or man-made lines—like roads, fences, or shadows—to guide the viewer’s eye directly to your subject.

3. Symmetry and Pattern Composition Techniques
Symmetry adds calm, while repetition creates rhythm. Master both for elegant, structured photos.

4. Framing in Photography Composition
Use windows, doorways, trees, or even shadows to frame your subject within the shot. It adds context and visual focus.

5. Cropping for Better Composition
Cropping eliminates distractions. It helps tighten your message and draw the viewer’s attention where you want it.

6. Depth in Photography Composition
Use foreground, middle ground, and background to build visual layers. It adds realism and immersion to flat images.

7. Using Contrast in Photography Composition
Contrast—light vs. dark, rough vs. smooth—helps define your subject and build visual drama.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
8. Mastering Negative Space in Composition
Leaving empty space around your subject gives the image room to breathe and emphasizes what matters most.

9. Fill the Frame Composition Technique
Get closer. By filling the entire frame with your subject, you eliminate distractions and intensify focus.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.