Introduction: The Beauty of Minimalism
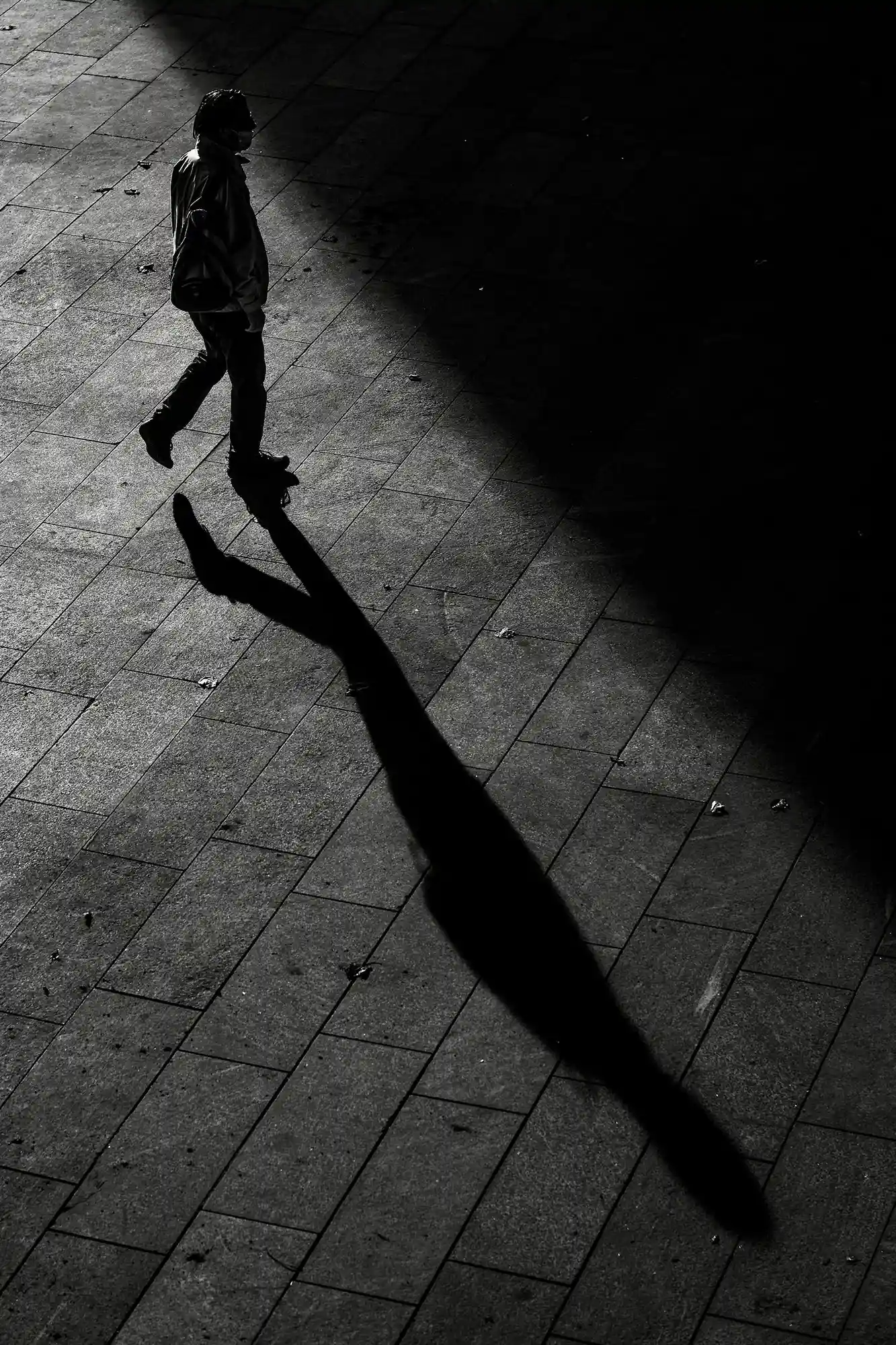
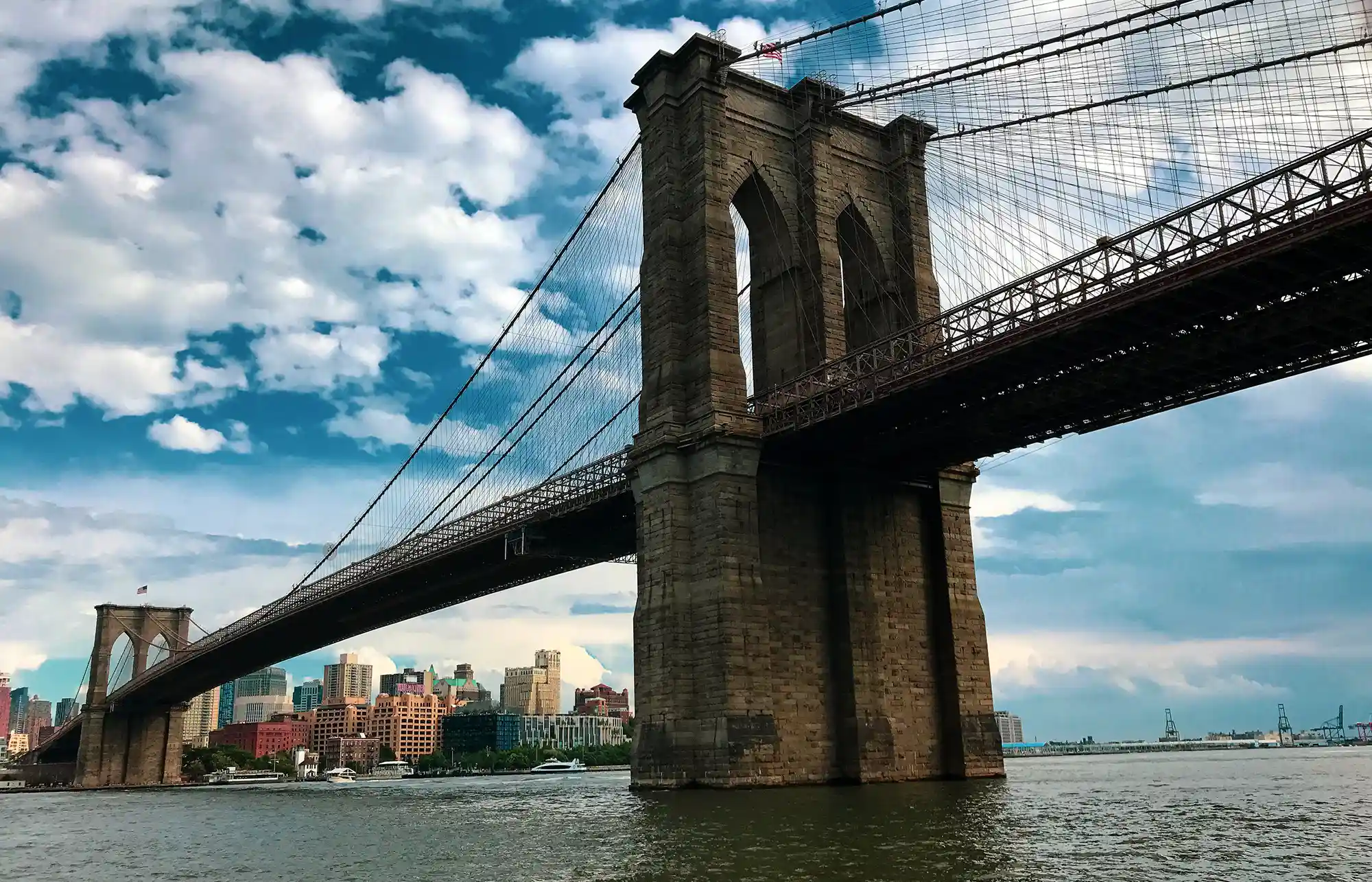
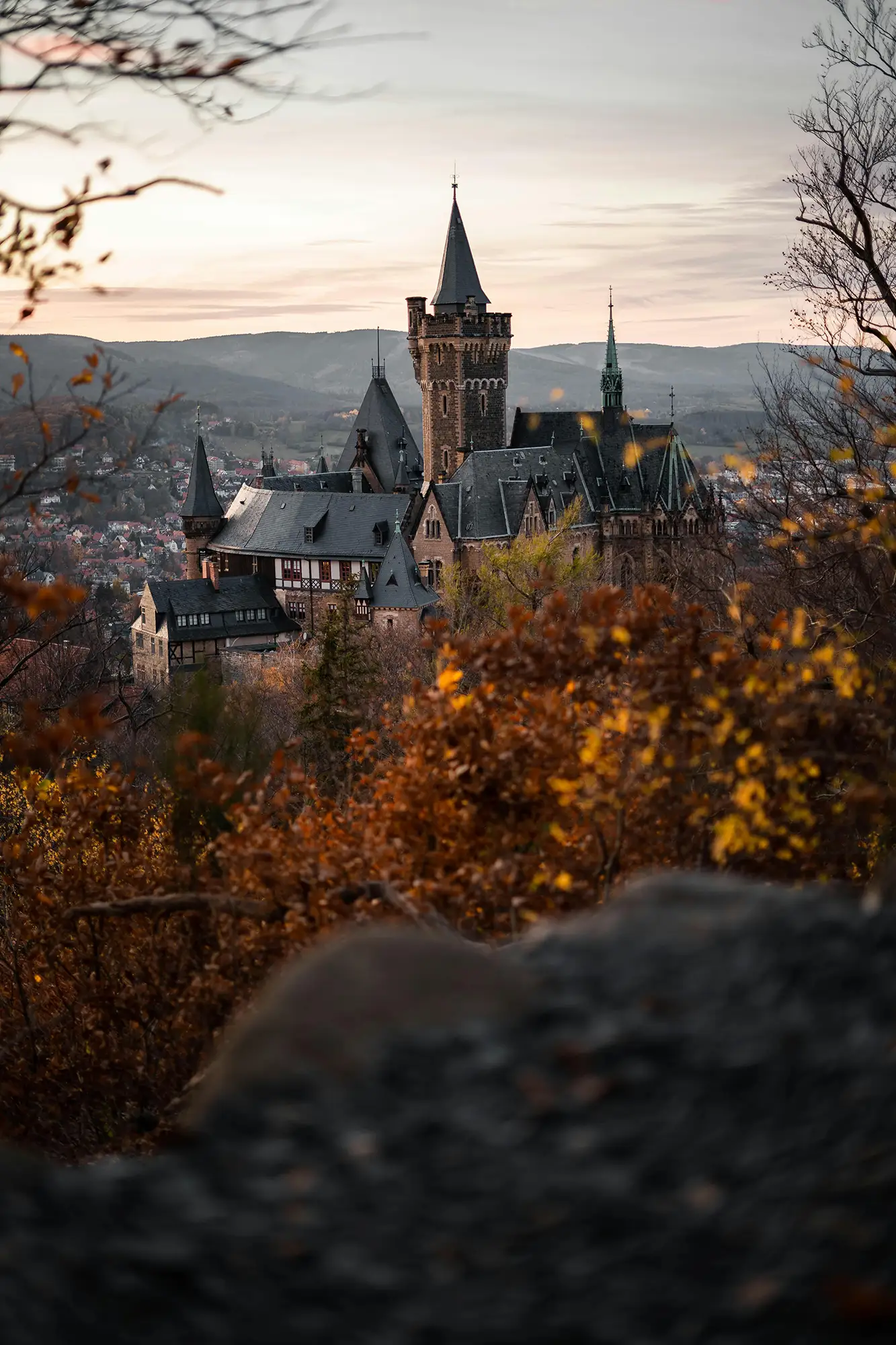
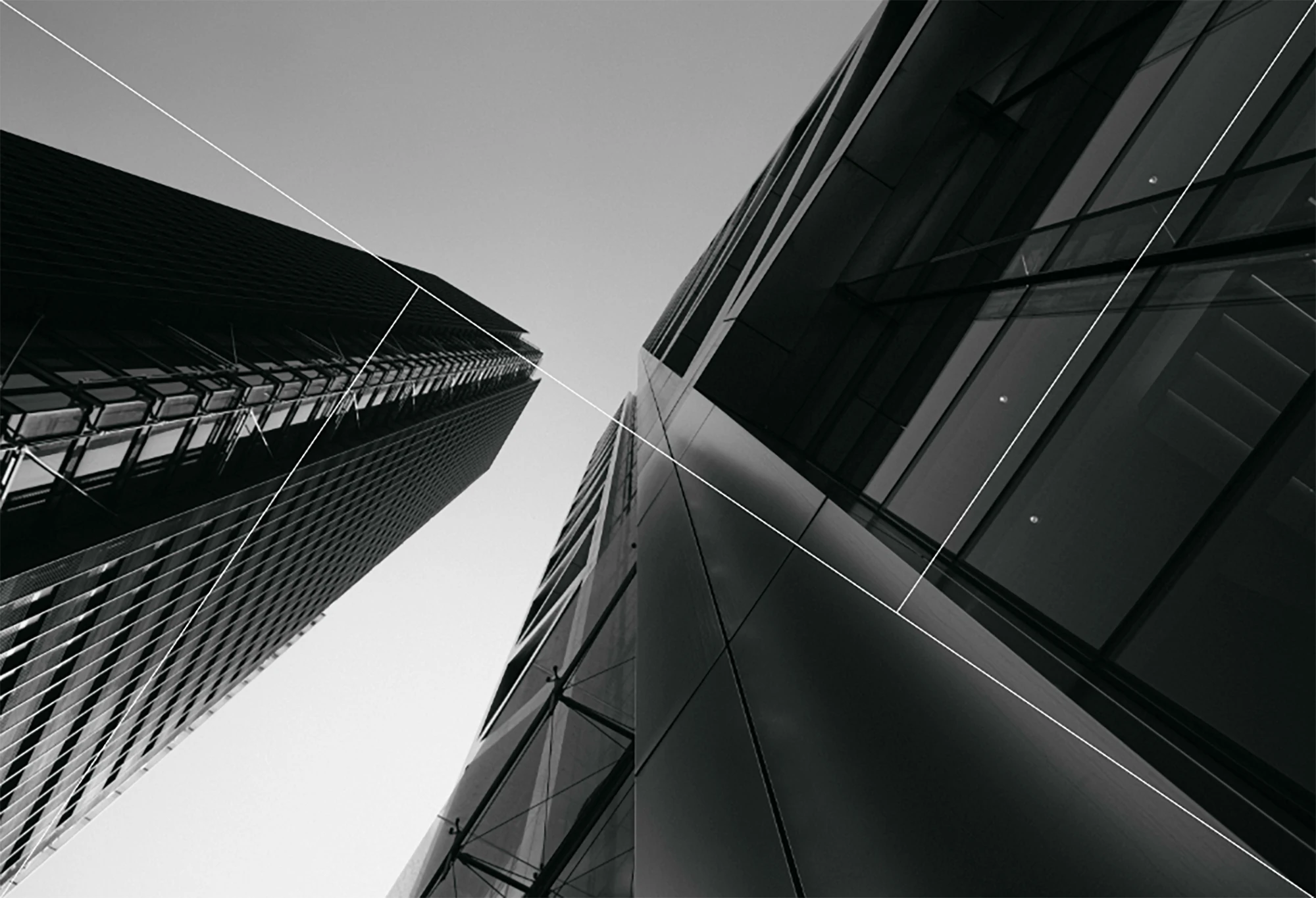
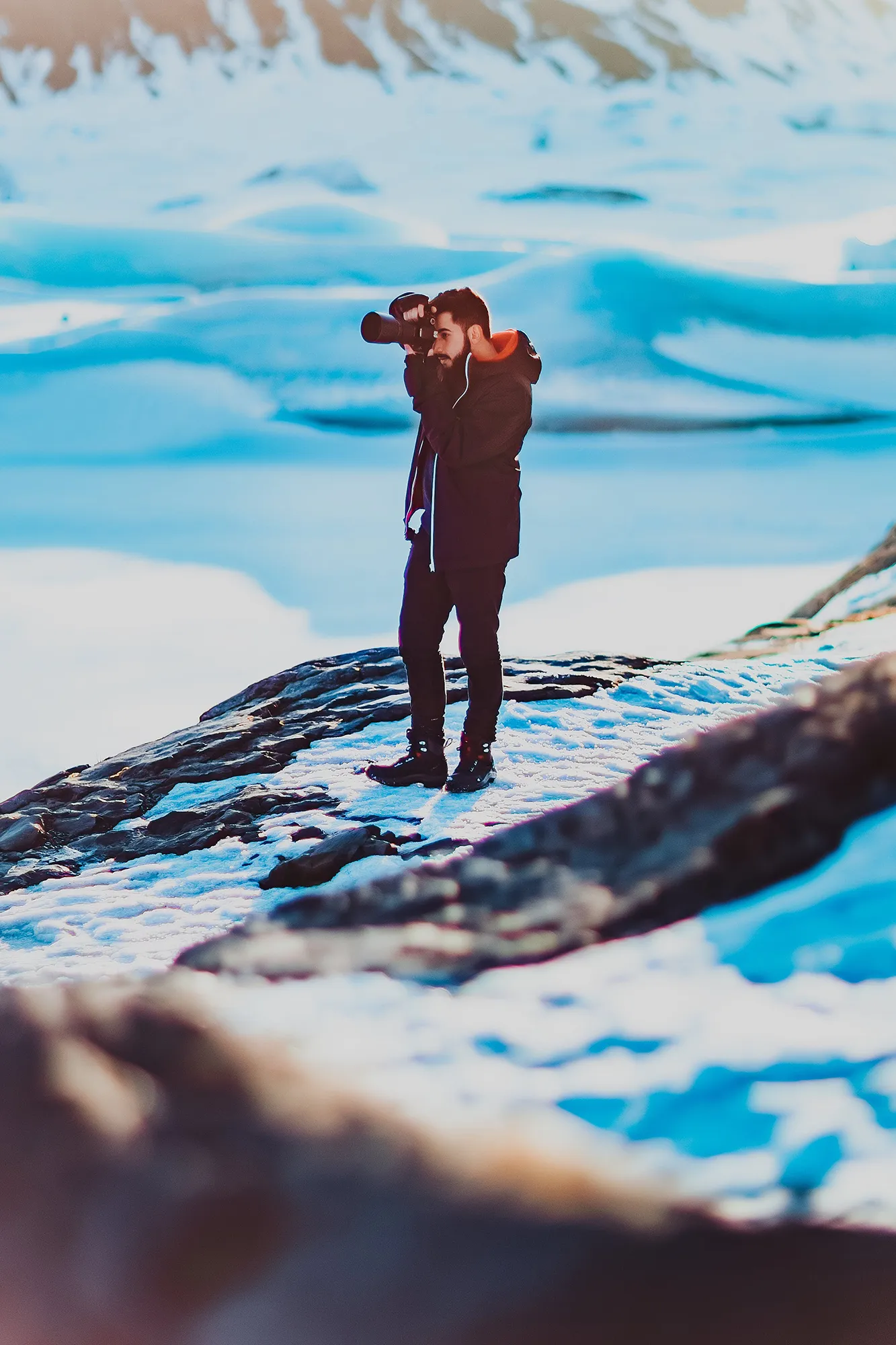
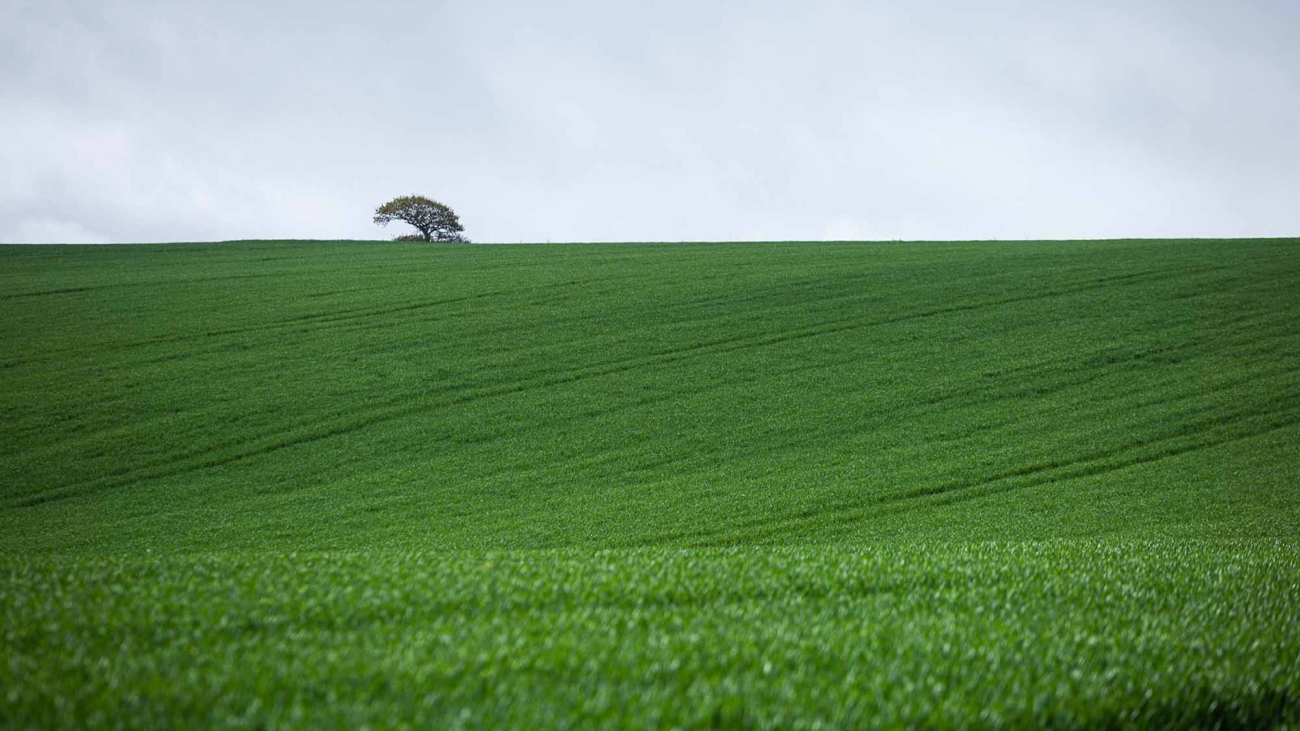
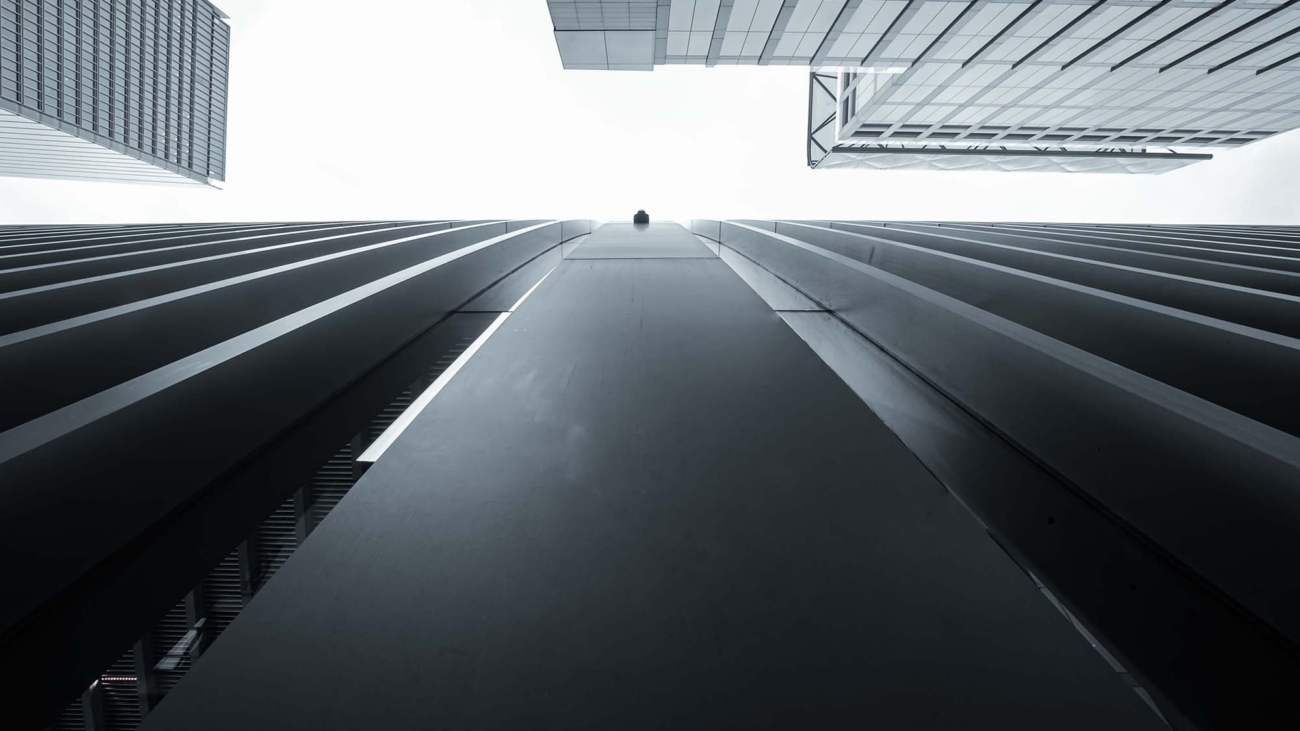
Minimalism in photography is an art form that focuses on simplicity and the deliberate use of space to convey a message or emotion. This guide explores how embracing minimalism can lead to powerful, thought-provoking images that resonate with viewers through their uncluttered and impactful compositions.
Understanding Simplicity and Minimalism
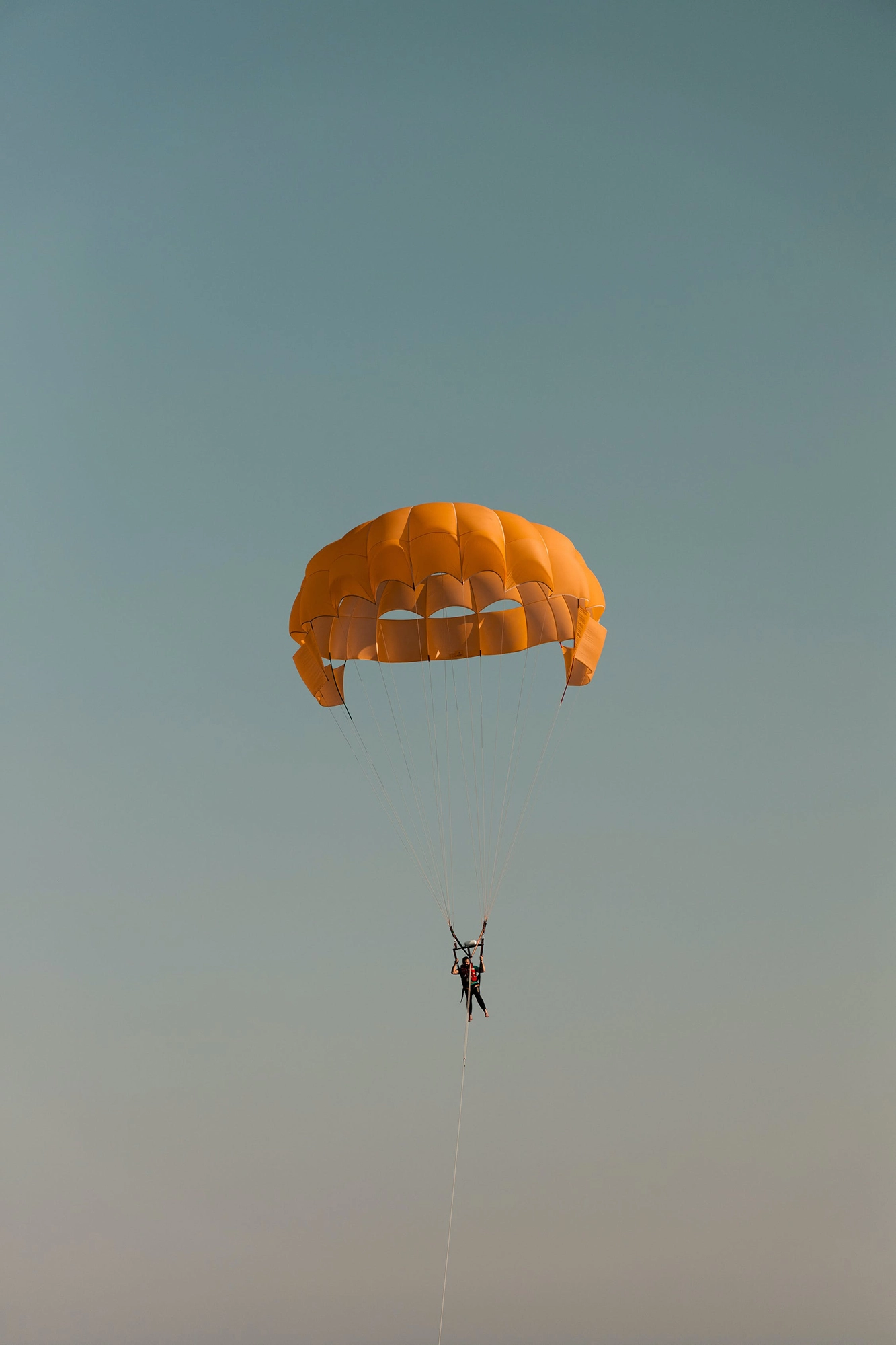
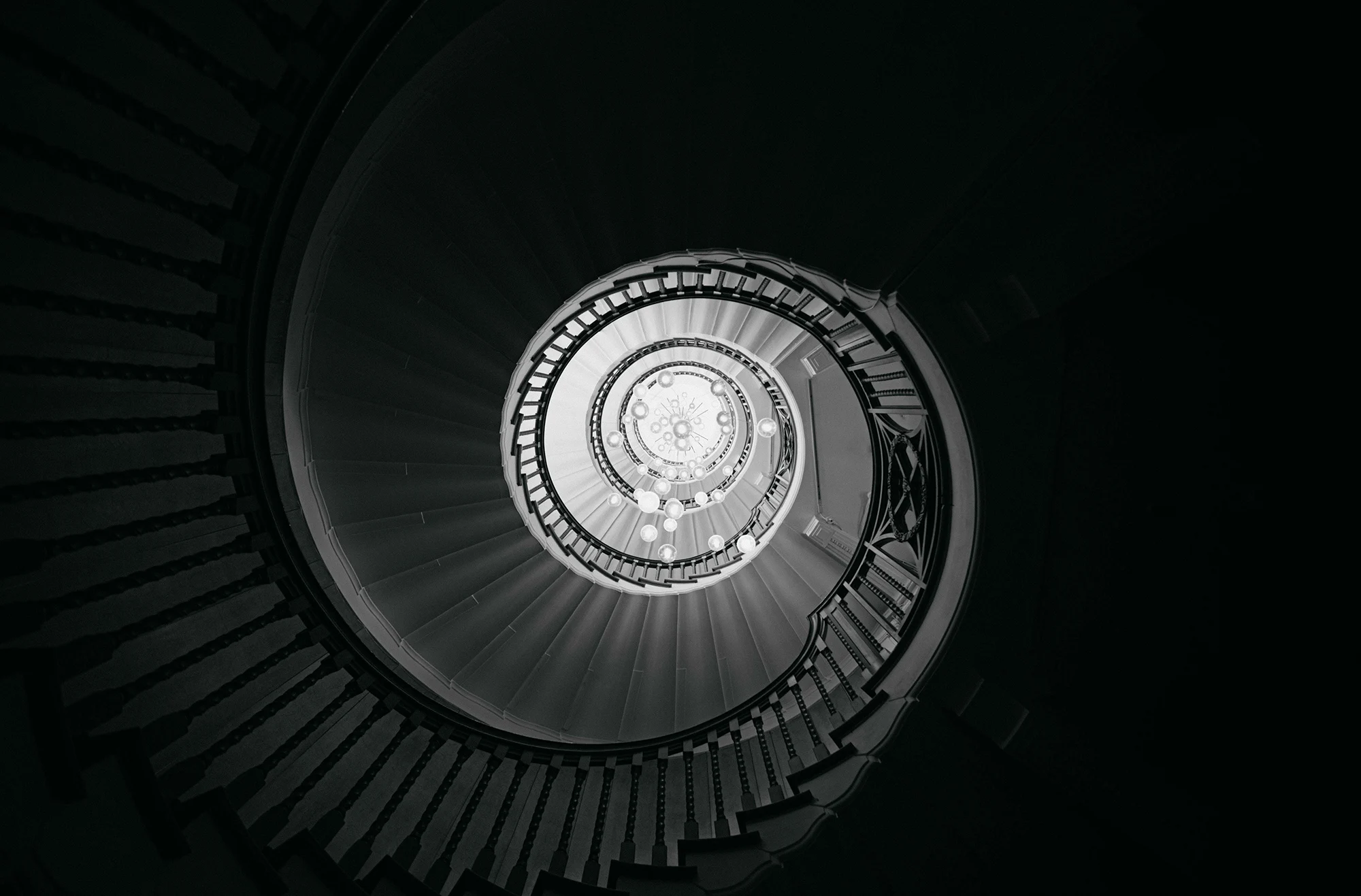
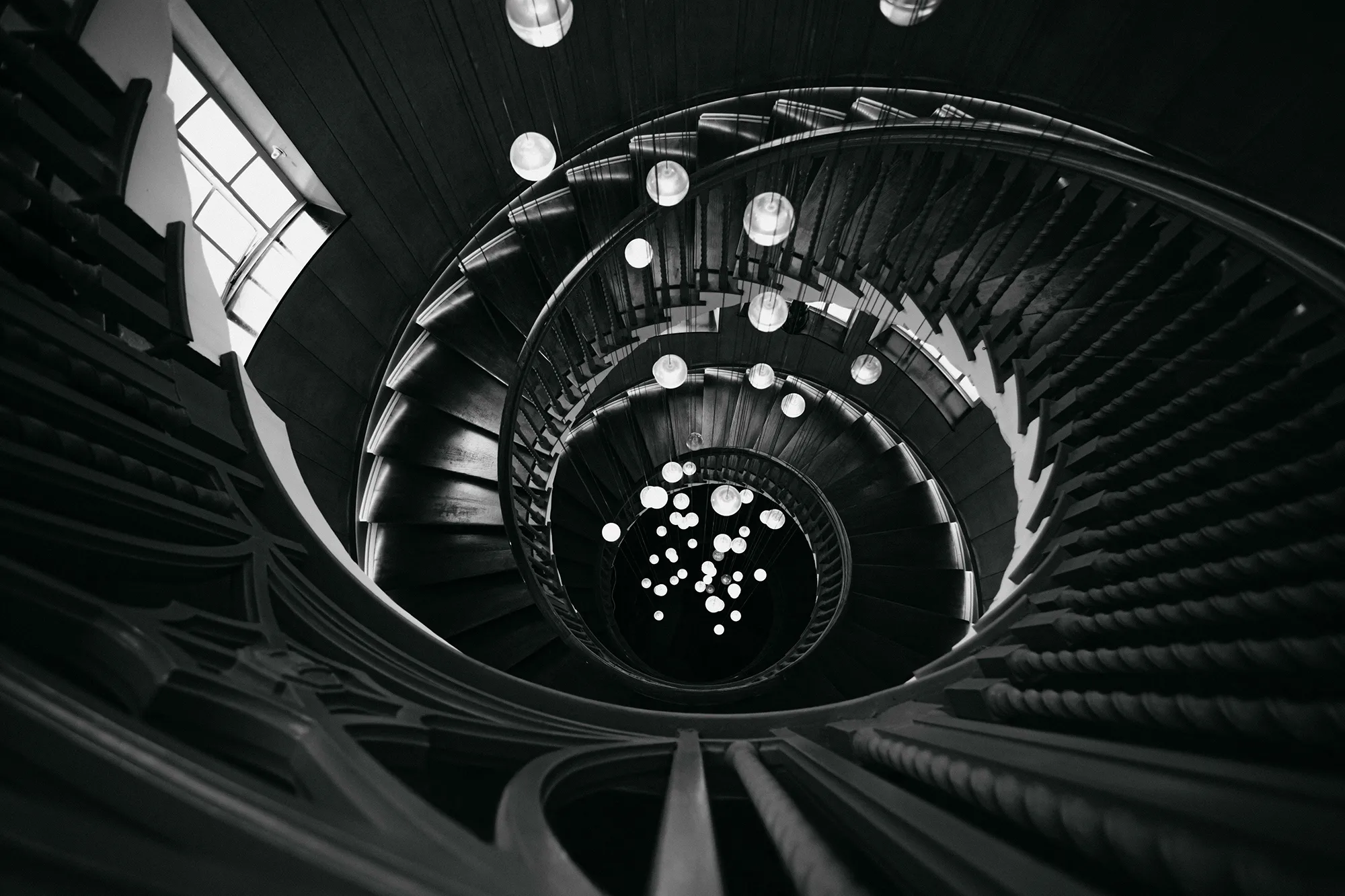
At its heart, minimalism is about stripping away the non-essential elements to highlight the beauty and uniqueness of the subject. It’s about finding strength in subtlety and conveying a narrative through the simplest of compositions.
Creative Process: Crafting Minimalist Photographs
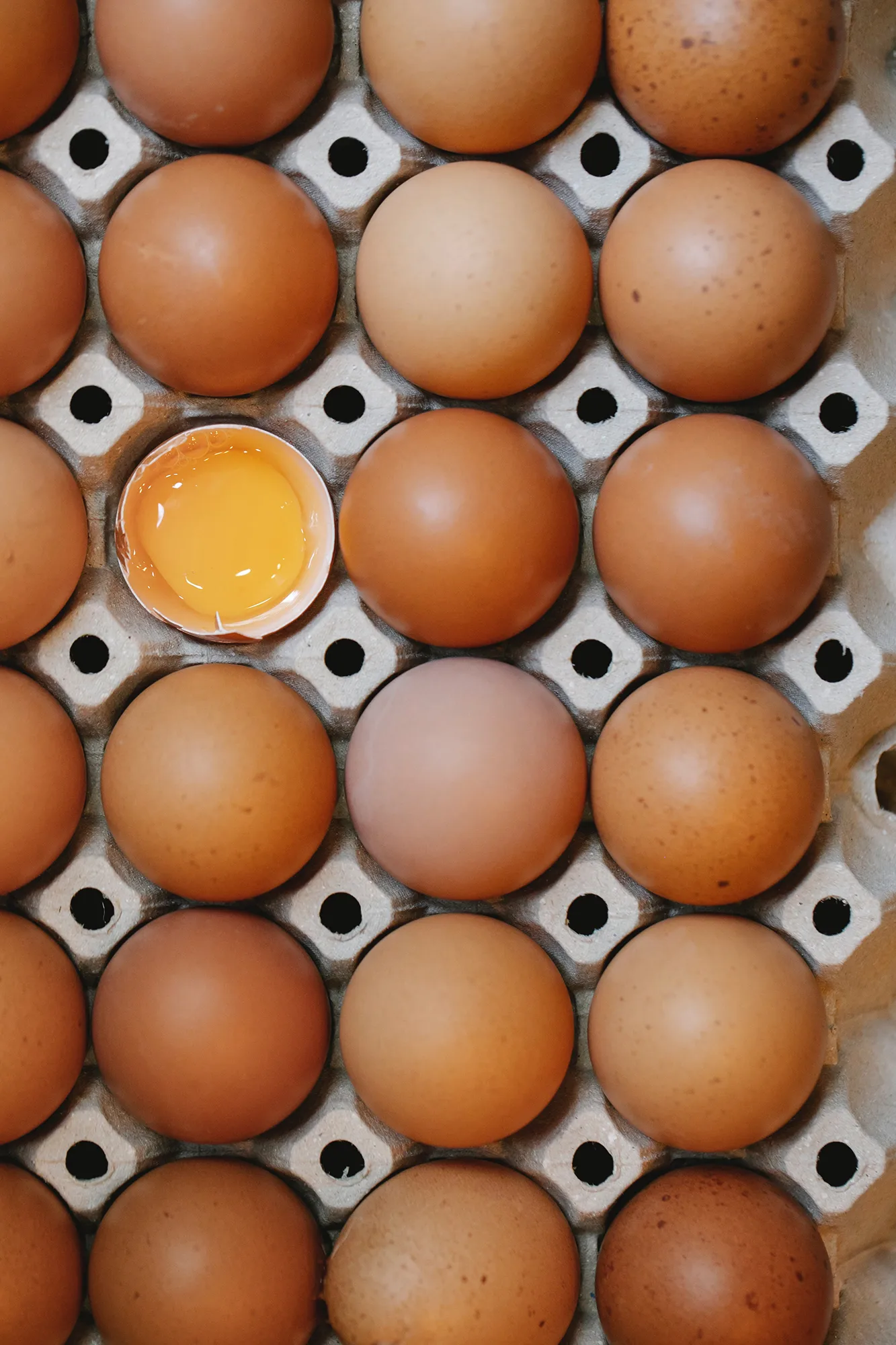
- Subject Selection: Choose subjects that stand out in their simplicity. Look for strong shapes, bold colors, or interesting textures.
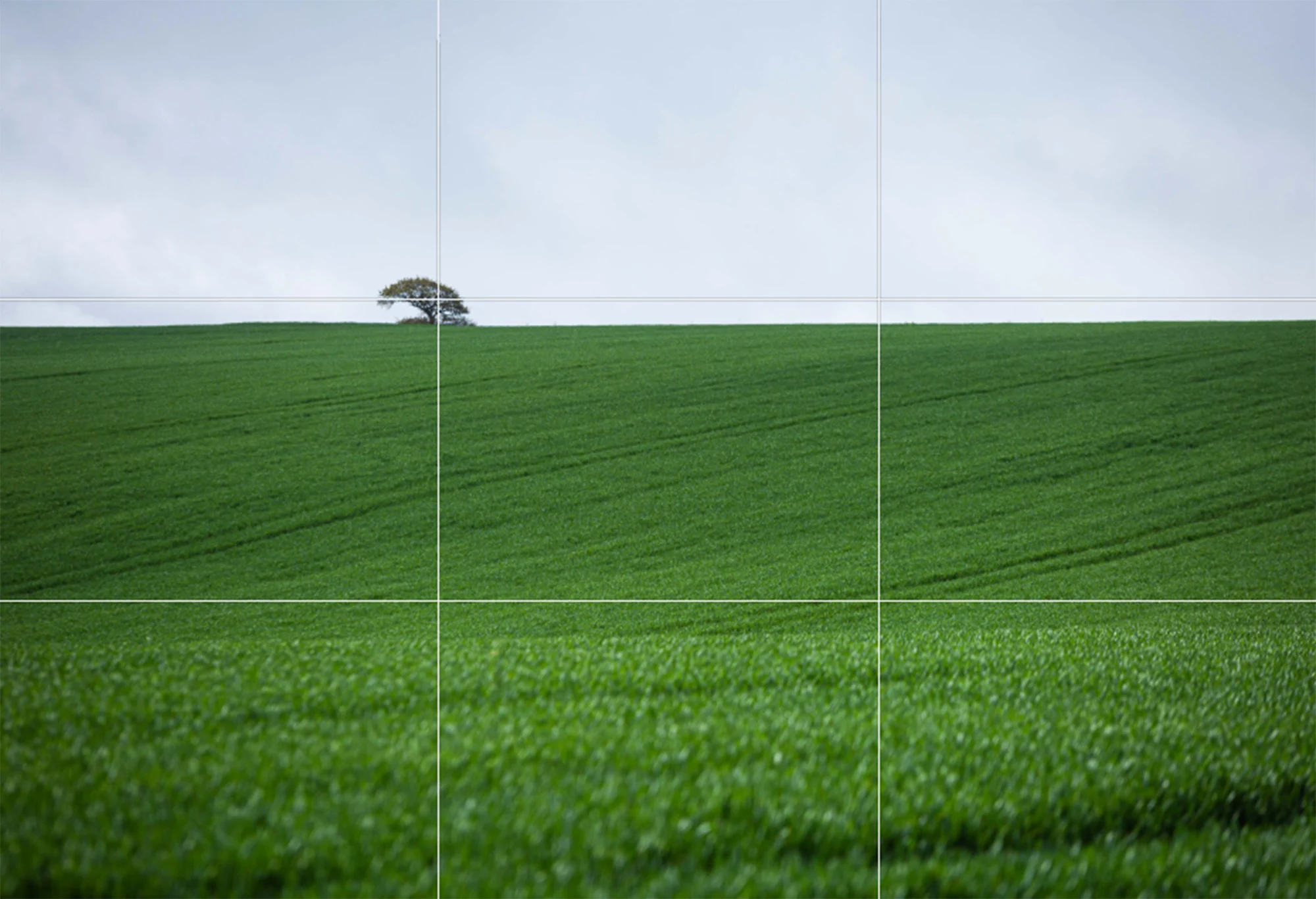
- Composition: Emphasize your subject by composing with plenty of negative space. Be intentional about what you include in the frame.
- Lighting: Use lighting to enhance the mood. Minimalist photos often benefit from soft, natural light or dramatic contrasts.
Tips for Photographers
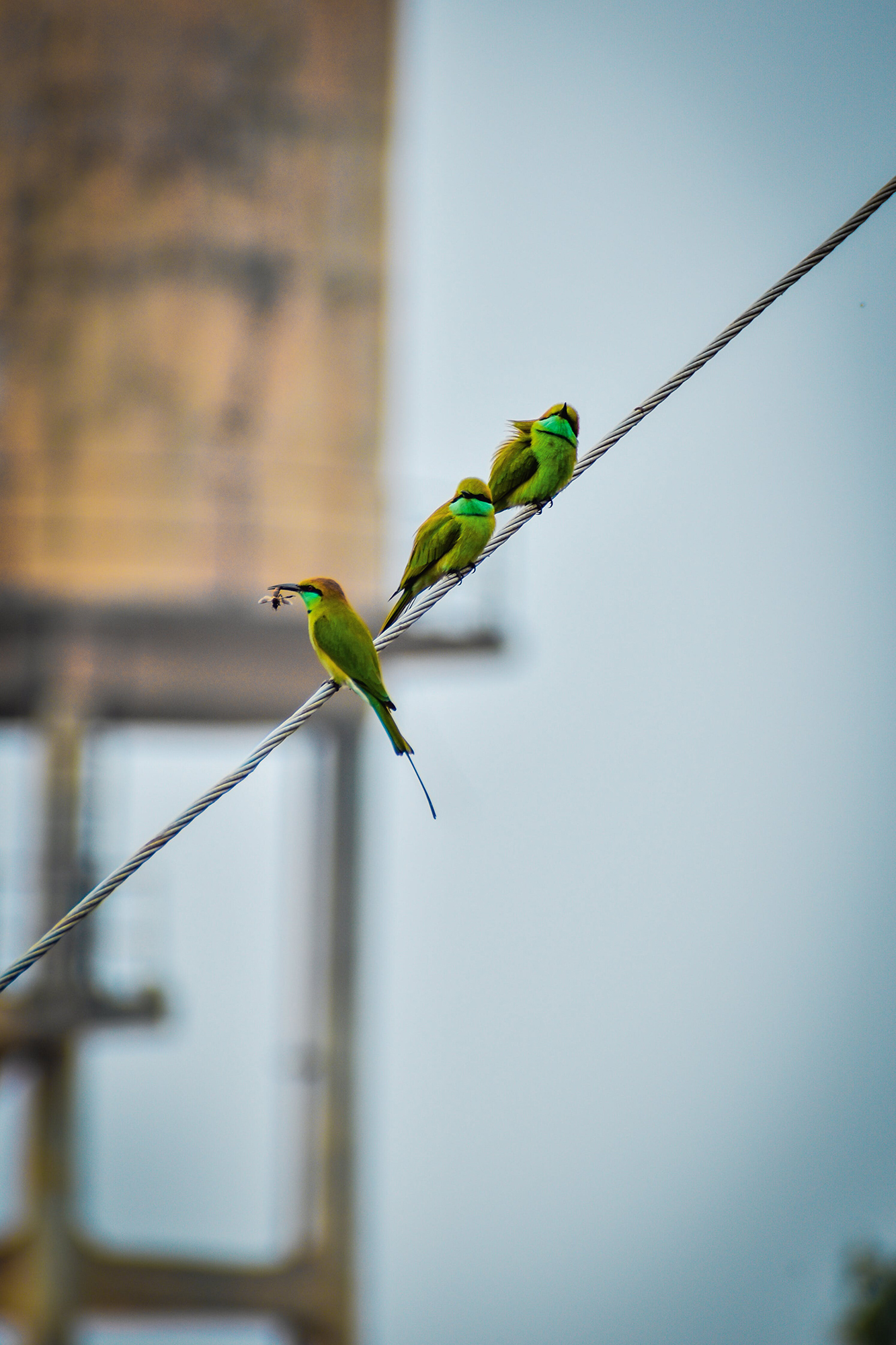
- Keep It Simple: Focus on one subject and remove any distracting elements from your frame.
- Pay Attention to Backgrounds: Choose backgrounds that are clean and unobtrusive to keep the focus on your subject.
- Experiment with Colors and Shapes: Use bold colors and simple shapes to create visually striking images.
- Practice Patience: Minimalist photography often requires patience to find the perfect subject or waiting for the right lighting conditions.
Advanced Techniques in Minimalist Photography
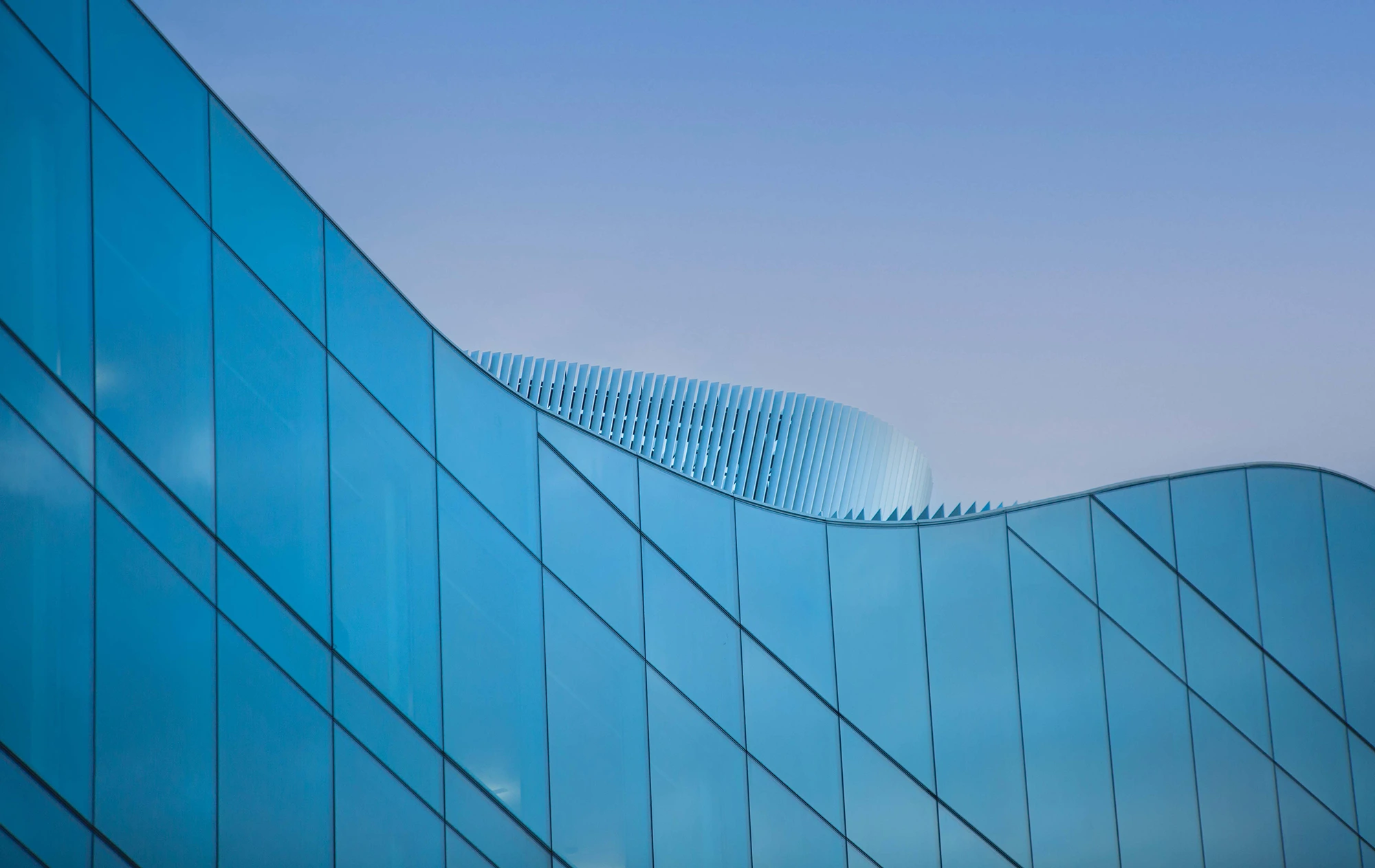
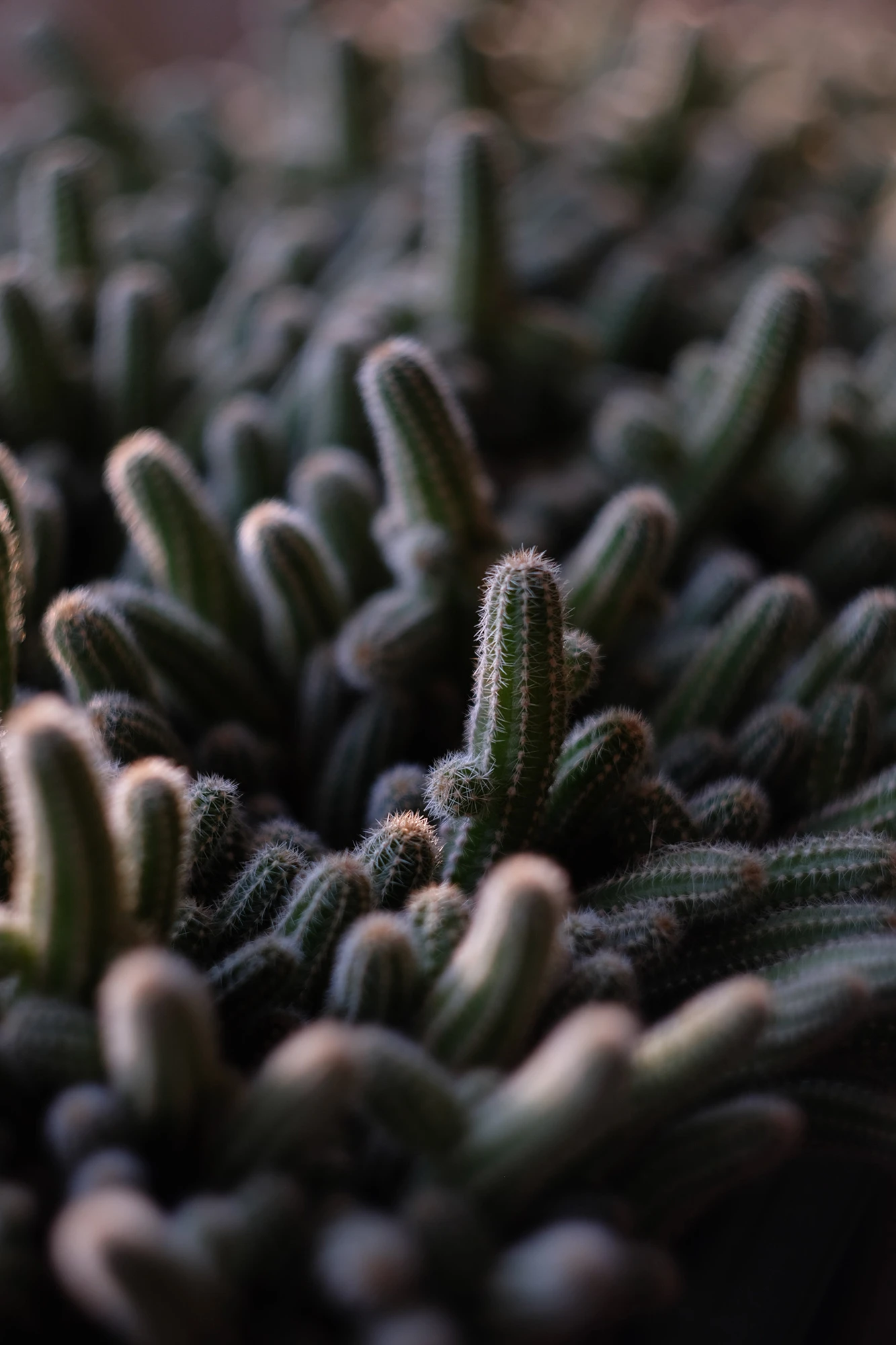
- Abstract Minimalism: Create abstract compositions that focus on shapes, colors, and textures rather than specific subjects.
- Monochromatic Themes: Experiment with monochromatic color schemes to enhance simplicity and focus.
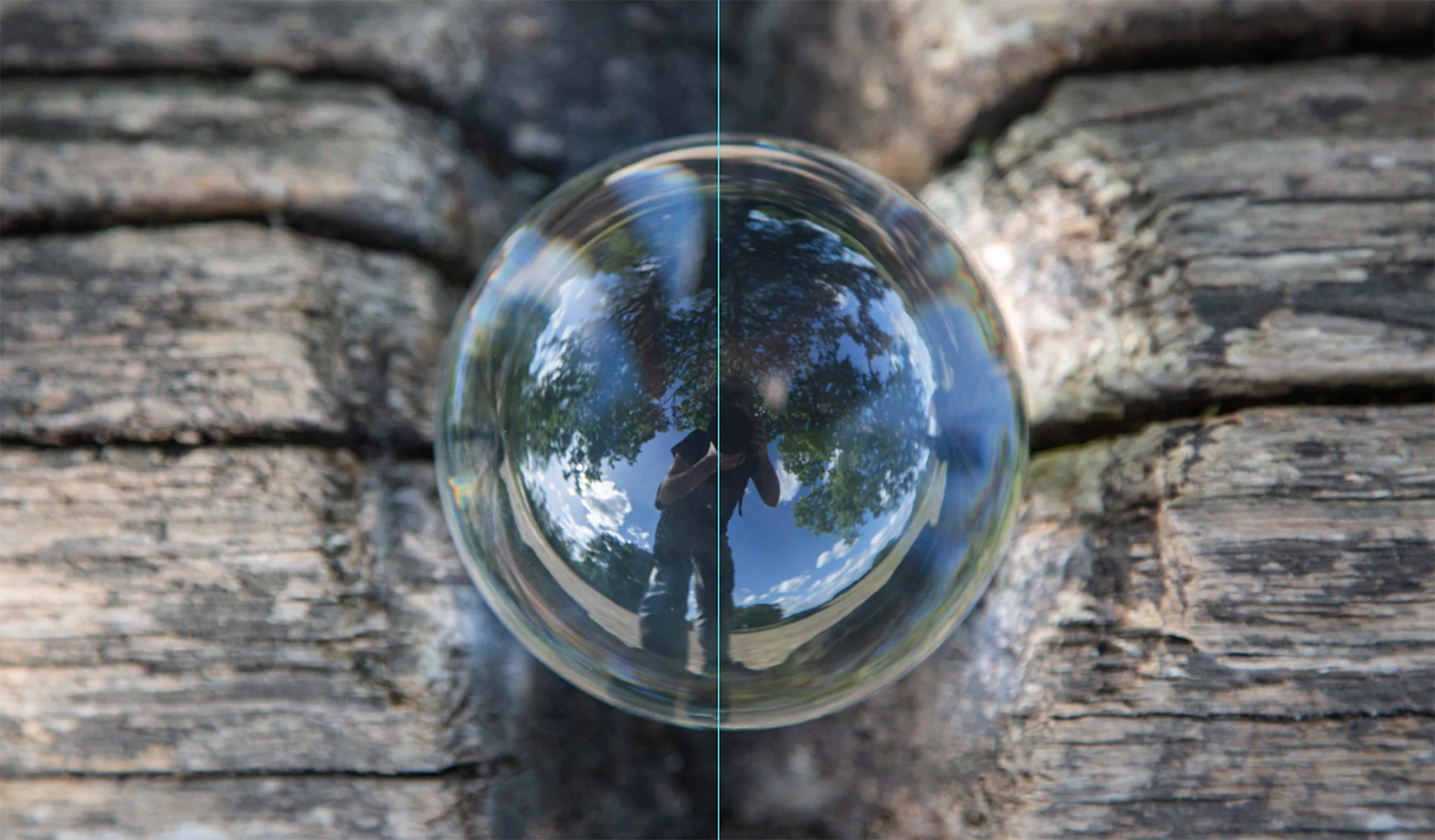
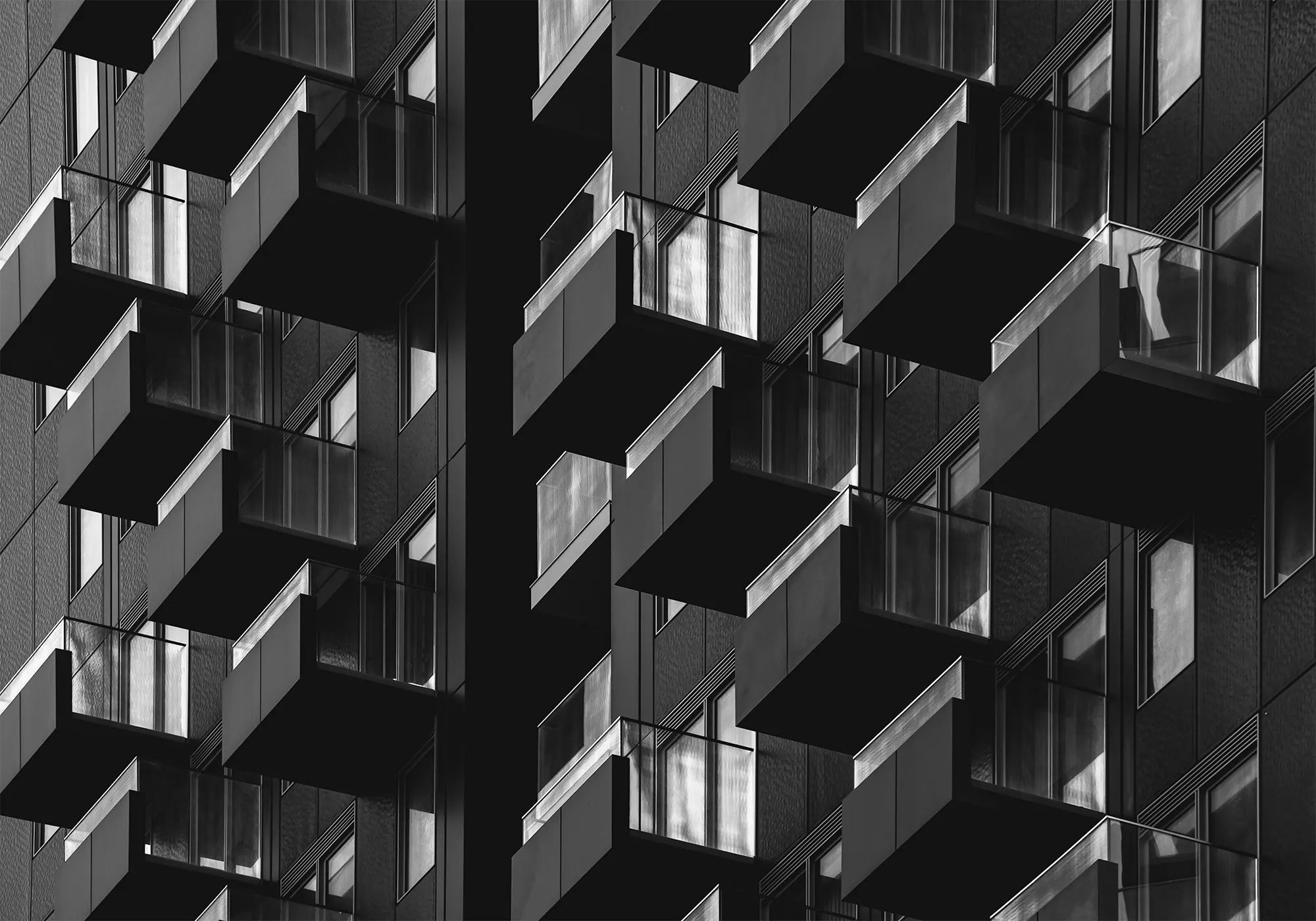
- Reflections and Shadows: Use reflections and shadows creatively to add depth and interest to minimalist compositions.
Practical Applications in Various Genres
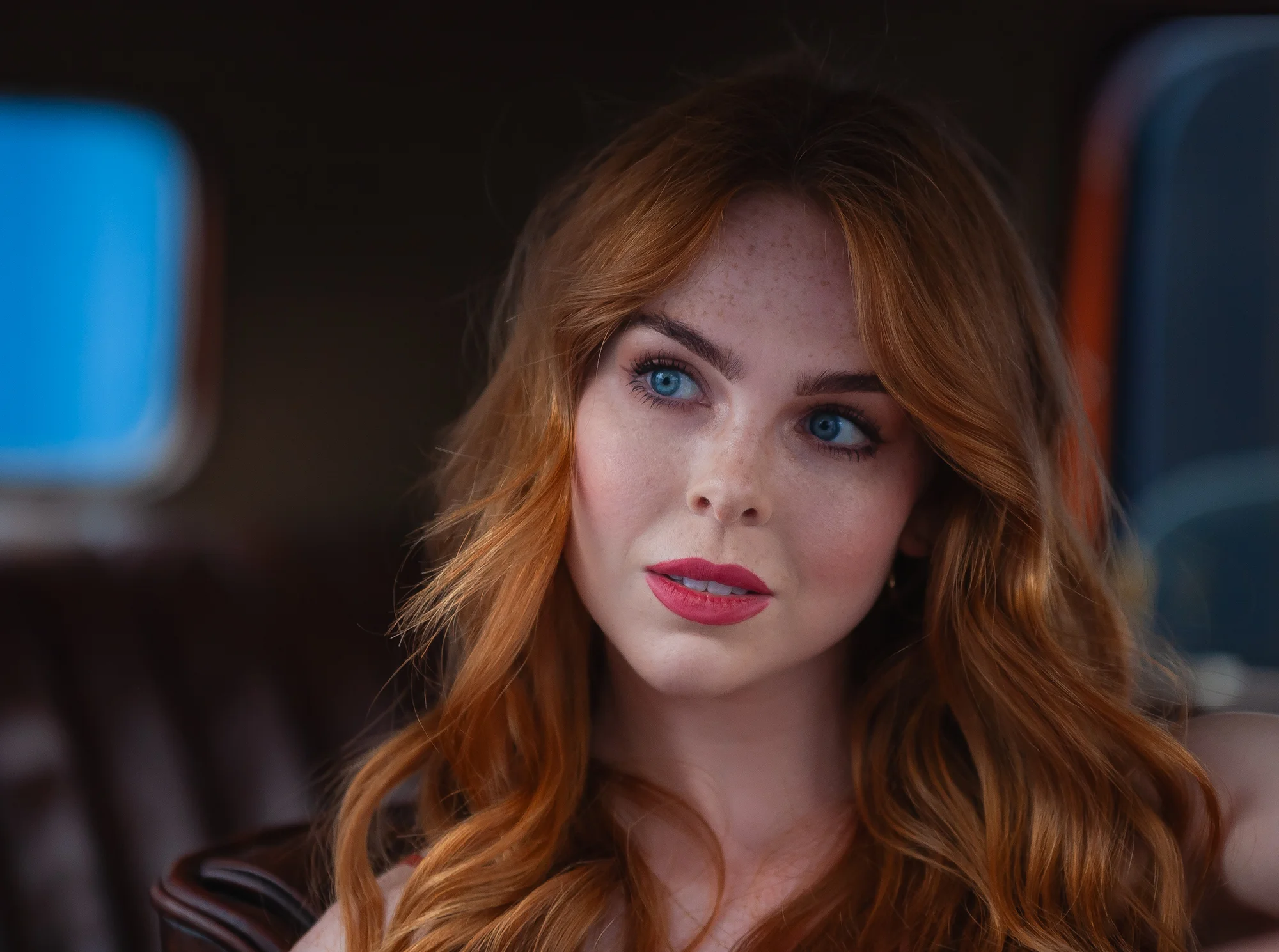
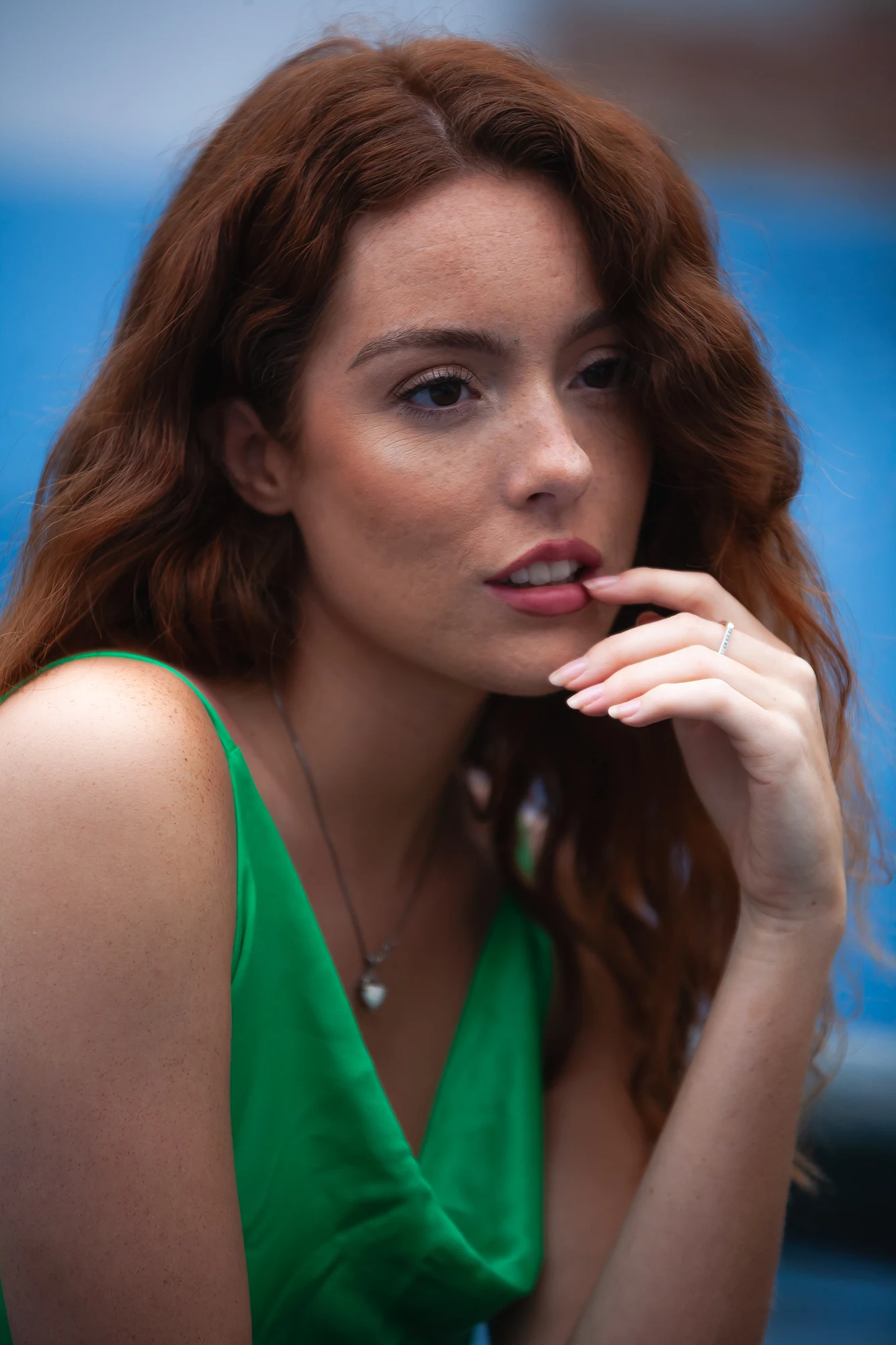
- Portrait Photography: Capture close-ups with simple backdrops or use the subject’s features as the main focal point.
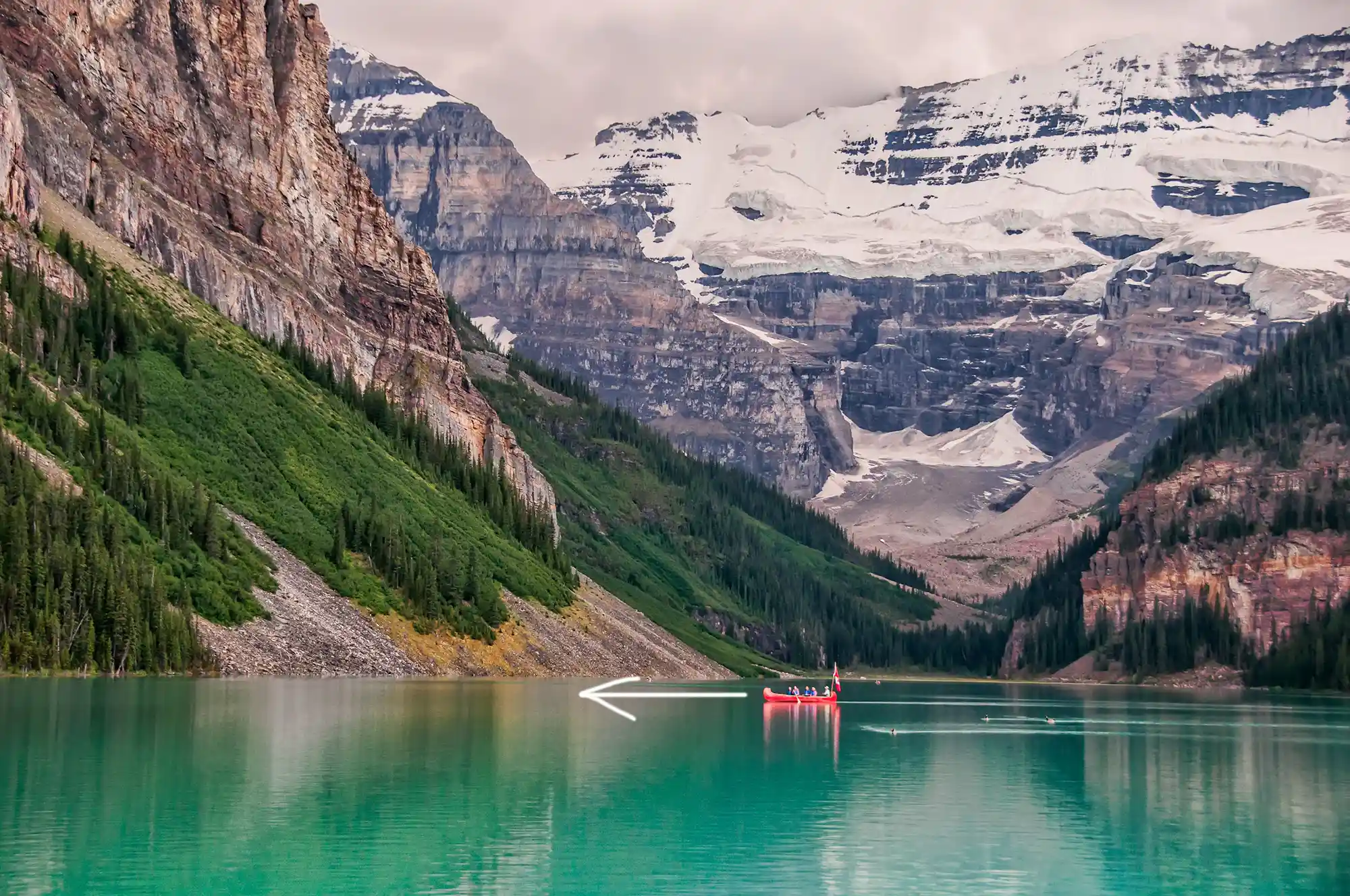
- Landscape Photography: Find simplicity in vast, open spaces or focus on a single natural element.
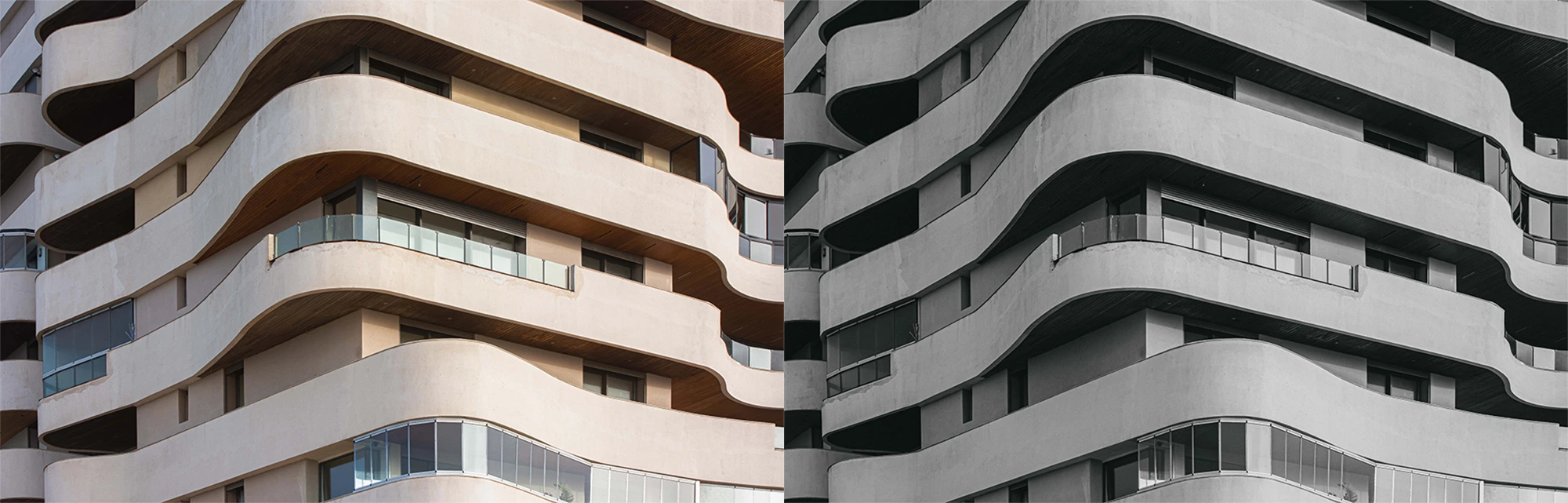
- Architectural Photography: Look for clean lines, geometric shapes, and contrasting textures in buildings and structures.
Conclusion: Embracing the Minimalist Approach
Minimalism in photography is about more than just taking pictures with few elements. It’s a mindset that values the beauty of simplicity and the power of understatement. By adopting a minimalist approach, photographers can create images that are both visually appealing and emotionally resonant.
O Carroll, B. (2016). 28 Composition Techniques That Will Improve Your Photos.
References
O Carroll, B. (2016). 28 Composition Techniques That Will Improve Your Photos. [online] PetaPixel. Available at:
https://petapixel.com/photography-composition-techniques/
[Accessed 13 December]