Introduction: The Art of Framing in Composition
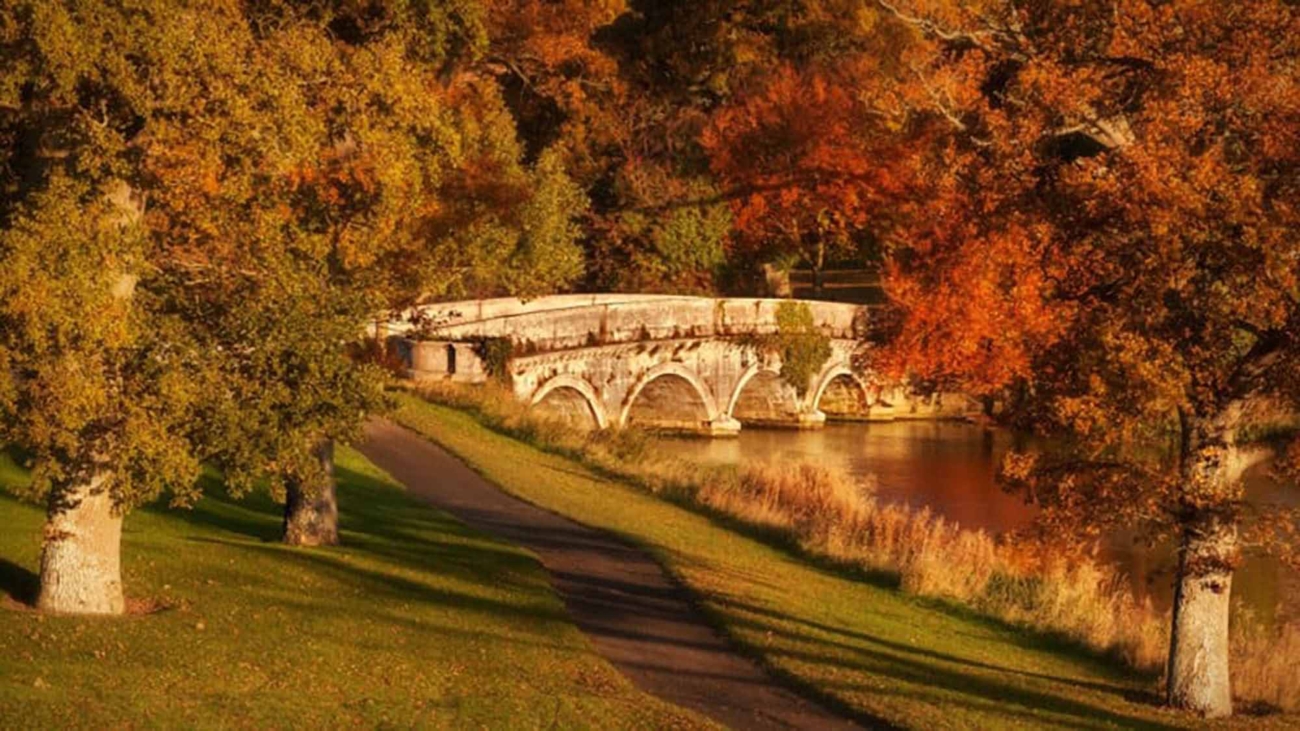
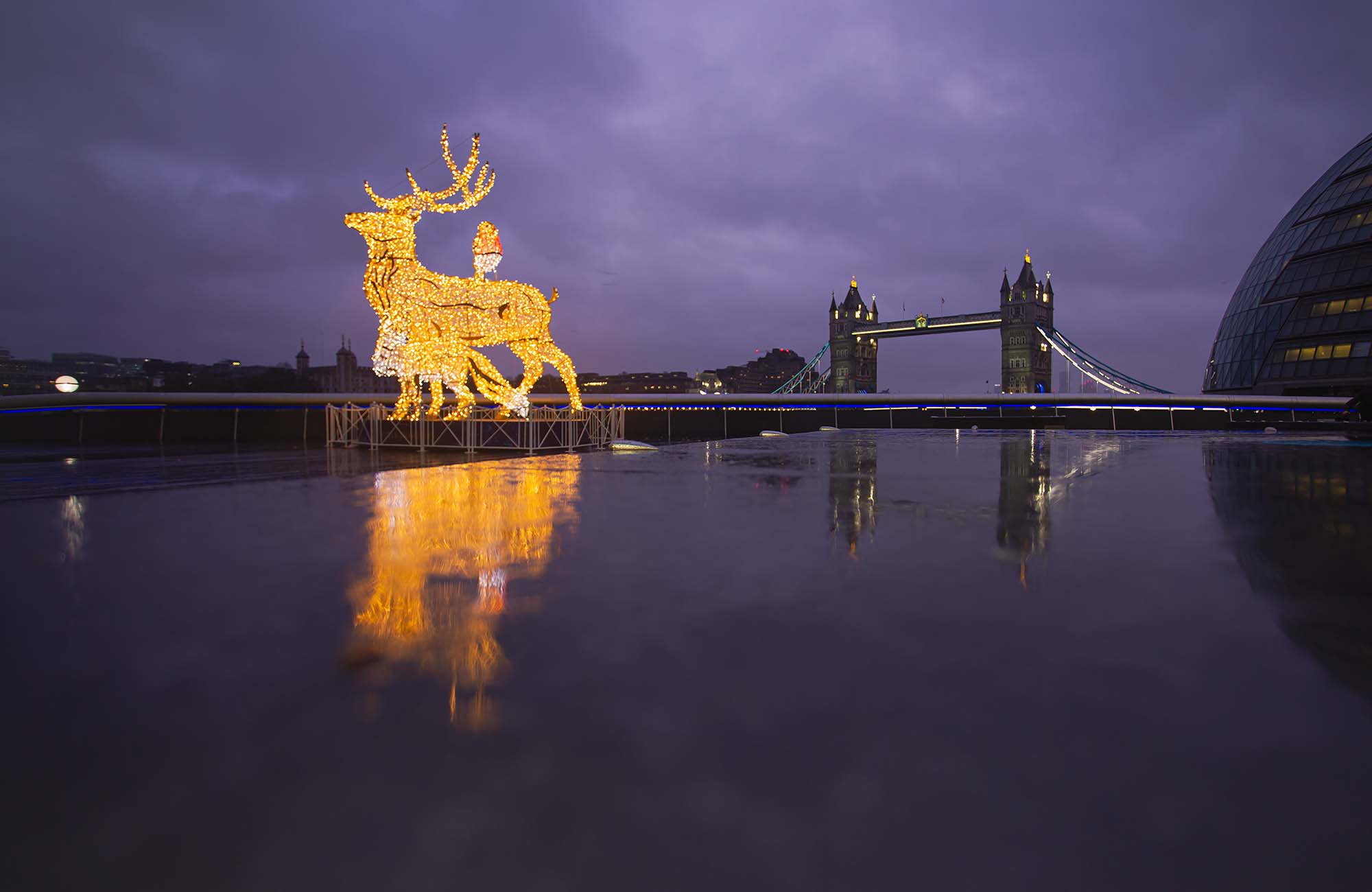
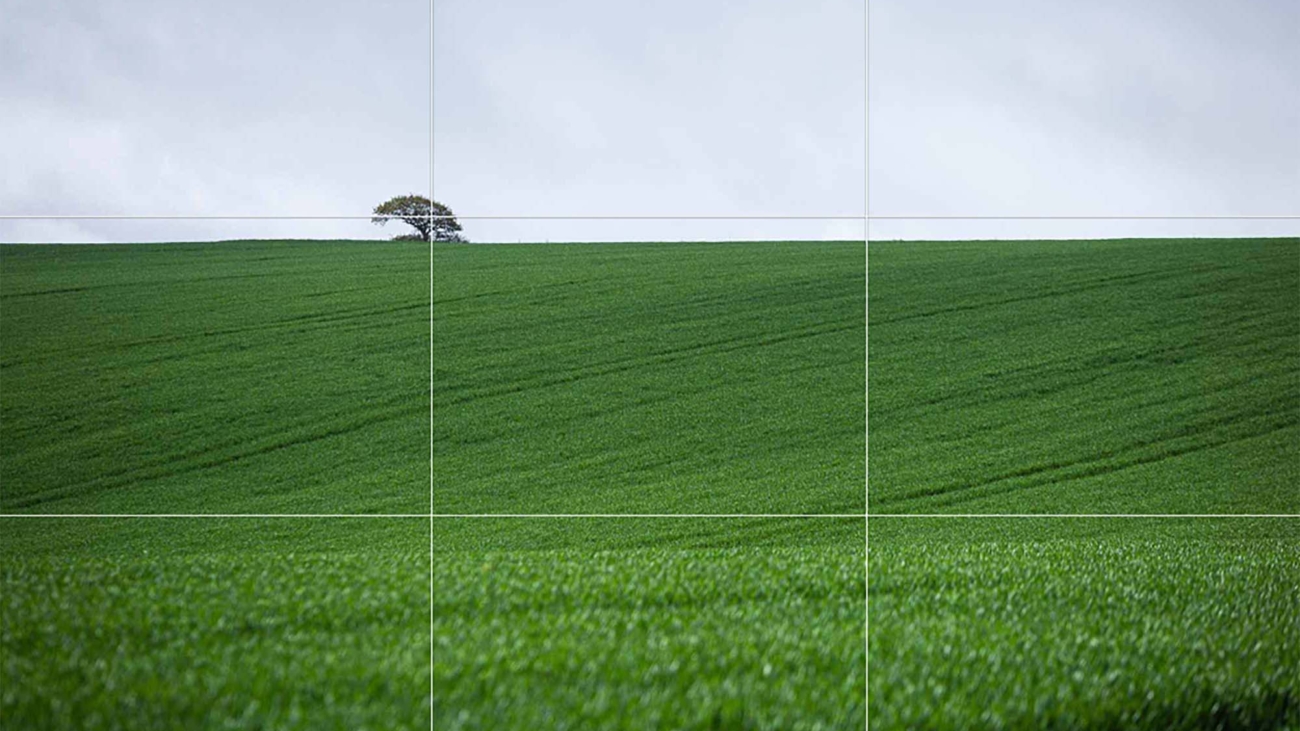
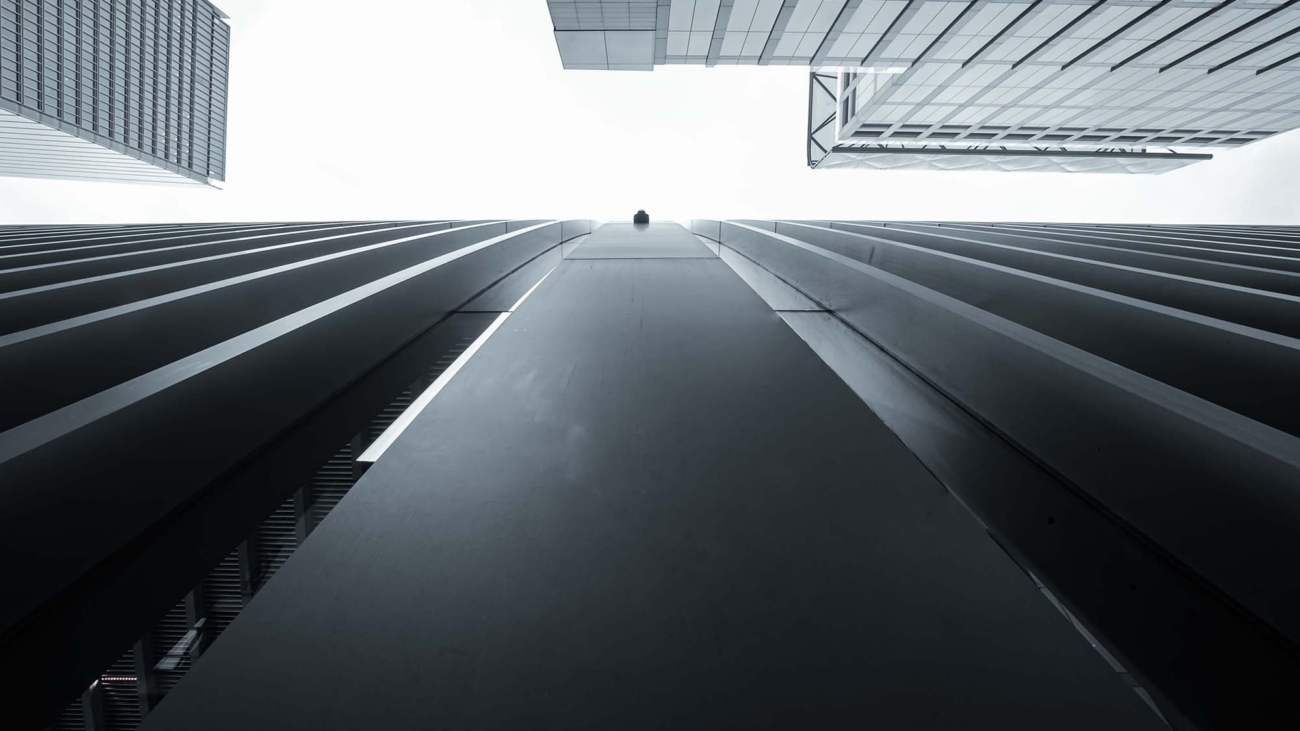
Framing within a frame is a compelling compositional technique that involves using elements within your scene to create a ‘frame’ around your subject. This method adds depth, context, and intrigue to your photographs, turning ordinary scenes into layered stories.
Understanding ‘Frame Within a Frame’
This technique is all about using elements in your environment, such as windows, doorways, arches, or even natural elements like tree branches, to create a secondary frame within your photograph. This inner frame leads the viewer’s eye to the primary subject, enhancing the narrative and depth of the image.

O Carroll, B. (2016). 28 Composition Techniques That Will Improve Your Photos.
Creative Process: Implementing Framing Techniques
- Identifying Framing Elements: Start by scouting for natural or architectural elements that can act as frames in your composition.
- Positioning Your Subject: Place your subject in a way that the framing element encapsulates or complements it, creating a focus point.
- Experimenting with Perspectives: Change your angle and perspective to see how different frames can alter the story or mood of your image.
Tips for Photographers
- Look for Unique Frames: Beyond windows and doors, look for unique framing opportunities like gaps in fences, reflections, or shadows.
- Play with Light and Shadow: Use light and shadows within your frame to add mood and emphasize your subject.
- Depth of Field: Experiment with different apertures to either blur the frame for a subtle effect or keep it sharp for a more pronounced framing.
- Balancing Elements: Ensure your frame complements the subject without overpowering it. The frame should lead to the subject, not distract from it.
Advanced Techniques in Framing
- Multiple Layers: Incorporate multiple layers of framing for a more complex and intriguing composition.
- Reflections as Frames: Use reflections in water, mirrors, or glass to create a unique framing effect.
- Contrasting Elements: Combine contrasting elements within your frame and subject for a dramatic effect.
Practical Applications in Various Genres
- Landscape Photography: Use tree branches or rock formations to frame a stunning vista or a setting sun.
- Urban Photography: Urban environments are rich with framing opportunities like bridges, tunnels, and building facades.
- Portrait Photography: Frame your subject with environmental elements to add context and depth to your portraits.
Conclusion: Refining Your Photographic Eye
Mastering the ‘Frame Within a Frame’ technique is a journey towards refining your photographic eye and enhancing your ability to tell stories through images. It requires practice, creativity, and an attentive observation of your surroundings.
References
O Carroll, B. (2016). 28 Composition Techniques That Will Improve Your Photos. [online] PetaPixel. Available at:
https://petapixel.com/photography-composition-techniques/
[Accessed 12 Dec. 2023]